Analysis of the SH3-Domain Kinase Binding Protein 1 Predictive Model for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and CCCTC-Binding Factor Transcriptional Regulatory Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2668Keywords:
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, SH3KBP1, Machine learning, Spatial transcriptomics, Single-cell RNA sequencing, Transcription factor CTCF, Multi-omics integrative analysisAbstract
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is among the most aggressive malignancies with extremely poor prognosis. This study systematically evaluates the expression patterns, biological functions, and regulatory mechanisms of the SH3-domain kinase binding protein 1 (SH3KBP1) in PDAC through multi-omics integrative analysis strategies.
Methods: Key predictive genes were identified using machine learning algorithms, including support vector machine (SVM), least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression, and SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP), based on multi-omics datasets. Validation analysis was performed using mRNA expression data from 179 PDAC tumor samples and 171 adjacent non-tumor samples (including four adjacent tissues and 167 normal controls), combined with proteomics data from 300 pairs of PDAC and non-tumor samples. Single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics analyzed cell-type-specific distribution and spatial localization characteristics of SH3KBP1. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) knockout experiments assessed functional dependency, and transcription factor binding site prediction explored upstream regulatory mechanisms. All analyses were performed on the R platform using specialized packages.
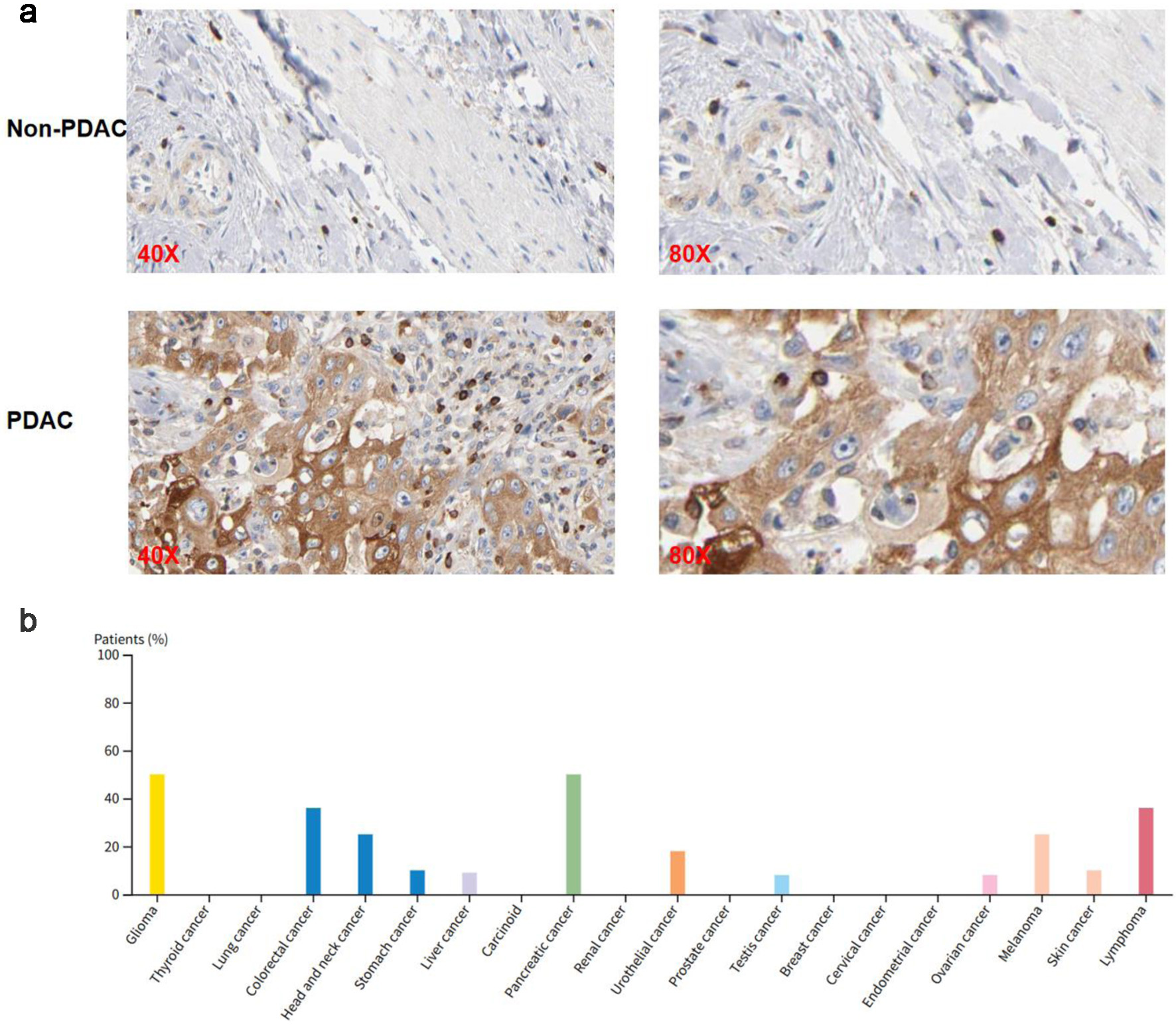
Results: Machine learning analysis successfully identified SH3KBP1 as a key predictive biomarker for pancreatic cancer. The gene was consistently selected by multiple algorithms. The constructed predictive model demonstrated excellent performance, with a maximum area under the curve (AUC) value of 0.994, and SHAP analysis further confirmed its important contribution to pancreatic cancer prediction. Validation analysis showed significant overexpression of SH3KBP1 in PDAC tumor tissues, with a diagnostic receiver operating characteristic curve AUC value reaching 0.985, demonstrating excellent diagnostic capability. Survival analysis revealed significant associations between high SH3KBP1 expression and poorer overall survival, disease-specific survival, and progress-free interval. Proteomics and immunohistochemistry analysis further confirmed significant upregulation of SH3KBP1 at the protein level. CRISPR knockout experiments revealed functional dependency of some PDAC cell lines on SH3KBP1. Single-cell RNA sequencing data showed that SH3KBP1 was mainly enriched in malignant epithelial cell populations with obvious copy number variation characteristics, and spatial transcriptomics analysis further confirmed its significant enrichment in tumor core regions. Transcriptional regulatory analysis suggested that transcription factor CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) may regulate SH3KBP1 transcriptional activity by binding to its promoter region, with both showing significant positive correlations in expression levels.
Conclusions: Via multi-omics integrative analysis, this study systematically elucidated the expression characteristics, spatial distribution, biological functions, and transcriptional regulatory networks of SH3KBP1 in PDAC, confirming its excellent diagnostic/prognostic value and potential as a PDAC molecular target, particularly involving the CTCF regulatory axis. It also provides a key theoretical basis for understanding how SH3KBP1-mediated signaling pathways (regulated by CTCF) drive pancreatic cancer development and progression.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









