Upregulated E26 Transformation-Specific Variant Transcription Factor 7 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Clinicopathological Correlations and Immune Regulatory Mechanisms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2606Keywords:
ETV7, Oral squamous cell carcinoma, Immunohistochemistry, Immune microenvironment, RNA sequencingAbstract
Background: E26 transformation-specific variant transcription factor 7 (ETV7) is implicated in various cancers, but its role in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remains undefined. This study explores the clinicopathological significance and molecular mechanisms of ETV7 upregulation in OSCC.
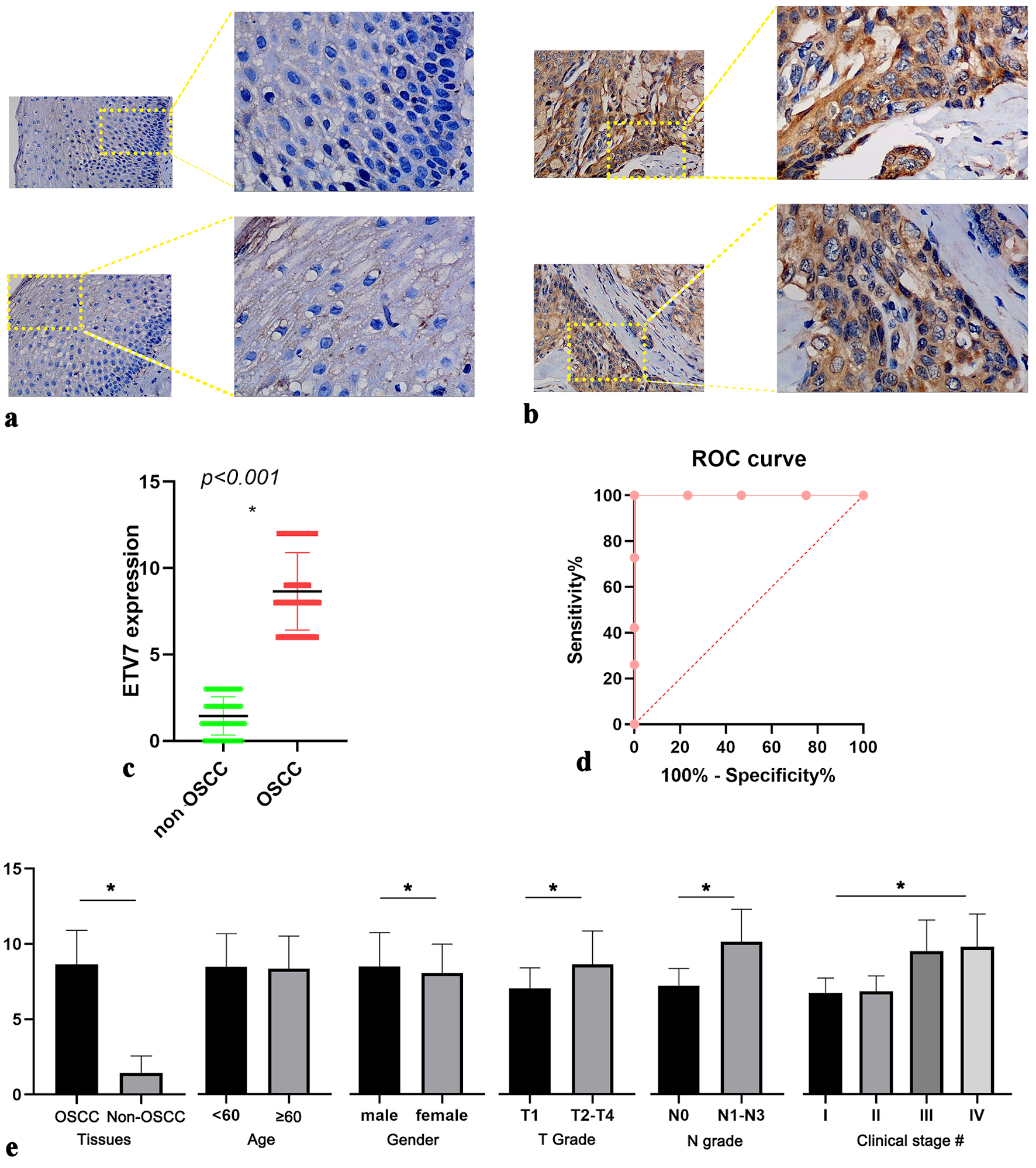
Methods: ETV7 protein expression was assessed via immunohistochemistry (IHC) in 173 OSCC and 60 non-OSCC tissues. ETV7 mRNA levels were analyzed using bulk RNA sequencing and single-cell RNA sequencing, supplemented by immune infiltration, enrichment and cell communication analysis.
Results: IHC revealed significantly higher ETV7 protein expression in OSCC than in non-OSCC tissues (P < 0.001), correlating with advanced T (r = 0.380, P < 0.001) and N stages (r = 0.592, P < 0.001). High-throughput data confirmed ETV7 mRNA upregulation (standardized mean difference (SMD) = 0.35, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.15 - 0.56; summary receiver operating characteristic (s receiver operating characteristic) area under the curve (AUC) = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.74 - 0.81), with levels decreasing twofold post-nivolumab treatment (P < 0.001). Enrichment analysis pinpointed the immune response-regulating signaling pathway as a key mechanism, supported by elevated immune cell infiltration (e.g., CD8+ T cells) in high-ETV7 samples. SLC15A4 and DAB2IP emerged as potentially overexpressed ETV7 targets. Cell communication analysis showed ETV7 enhancing myeloid cell interactions via the midkine (MK) pathway.
Conclusions: ETV7 upregulation drives OSCC progression, potentially through immune microenvironment modulation, positioning it as a candidate biomarker and therapeutic target. Its association with clinical stage and immunotherapy response underscores its prognostic relevance in OSCC management.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









