Identification of Genes and Construction of Prognostic Model of Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Propionate Metabolism-Related Genes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2680Keywords:
LUAD, Propionate metabolism, Hub genes, Prognostic model, BioinformaticsAbstract
Background: Dysregulation of propionate metabolism can enhance the invasive properties of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) cells and increase their metastatic potential. Therefore, we constructed a predictive model based on propionate metabolism-related genes (PMRGs) to evaluate the prognosis of patients with LUAD.
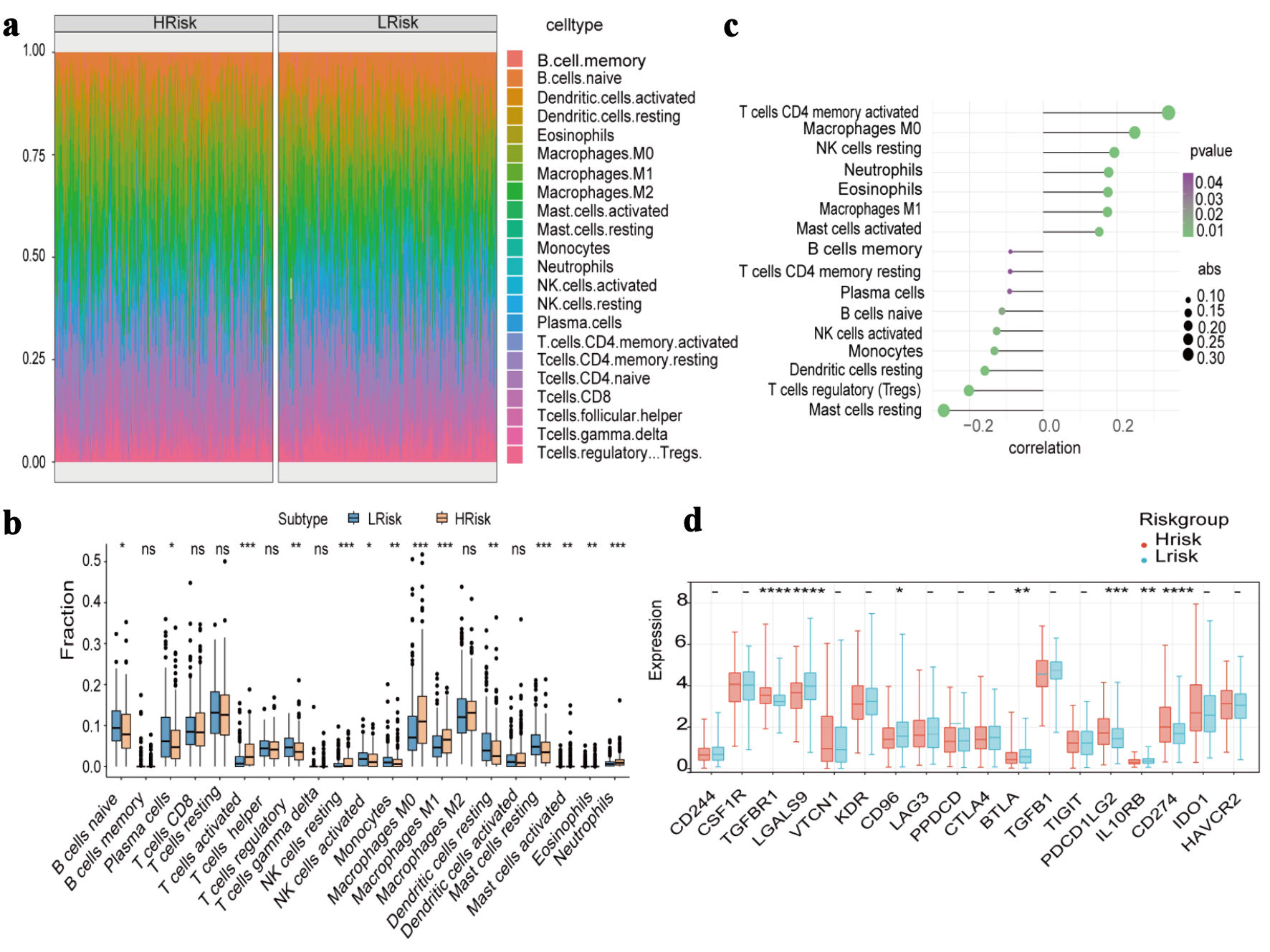
Methods: mRNA expression profiles and clinical data of LUAD patients were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). The predictive model was constructed using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO). The associations between the risk score and tumor prognosis, immune infiltration, drug sensitivity, signaling pathways, and clinical features were evaluated using the CIBERSORT algorithm, the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC) database, gene set variation analysis (GSVA), gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), and nomogram analyses. For hub genes, motif enrichment, genome-wide association study (GWAS) analysis and single-cell analysis were performed. Expression differences between LUAD cells and normal lung epithelial cells were validated using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
Results: We established a LUAD prognostic model containing 16 hub genes. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) values for the model were 0.722 (1-year overall survival (OS)), 0.696 (3-year OS), and 0.700 (5-year OS). GSVA revealed significant enrichment in the G2/M checkpoint, E2F targets, and glycolysis pathways. GSEA indicated enrichment of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1), interleukin (IL)-17, and p53 signaling pathways. Transcription factor analysis identified the motif cisbp-M4287 as the most significantly enriched, with a normalized enrichment score (NES) of 5.9. qRT-PCR results showed that the expression of ADIPOQ, CYP27A1, and GCDH was downregulated, while the expression of SERPINE1 was upregulated. No statistically significant differences were observed in the expression of CYP17A1 and EHHADH.
Conclusions: A novel prognostic model based on PMRGs was established to predict overall survival in LUAD patients.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









