Liquid Plasma Induces Necroptosis Without Inflammatory Responses in Head and Neck Cancer Cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2579Keywords:
Liquid plasma, Necroptosis, Head and neck cancer, Inflammation, TreatmentAbstract
Background: Several types of regulated cell deaths are known, including apoptosis, necroptosis, autophagy, ferroptosis, and pyroptosis. Among these types of cell deaths, apoptosis is induced by many cancer therapeutic agents. In the case of resistance, however, induction of other regulated cell death, such as necroptosis, are required. Liquid plasma, which is prepared by treatment of non-thermal plasma to solution, induces various types of regulated cell death via reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.
Methods: Liquid plasma was generated by N2/Ar plasma treatment in culture medium (minimum essential medium (MEM), Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM), or Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI)-1640) for 120 s per milliliter of medium (2 cm). Cell viability was determined using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8), and apoptosis was determined by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), cycloheximide (CHX), and zVAD-fmk were used to induce necroptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cells, and necroptosis inhibitors, such as necrostatin-1 (Nec-1, 50 µM), GSK872 (10 µM), and necrosulfonamide (NSA, 2 µM) were used to inhibit necroptosis. Statistical comparisons between groups were carried out using the Student’s t-test.
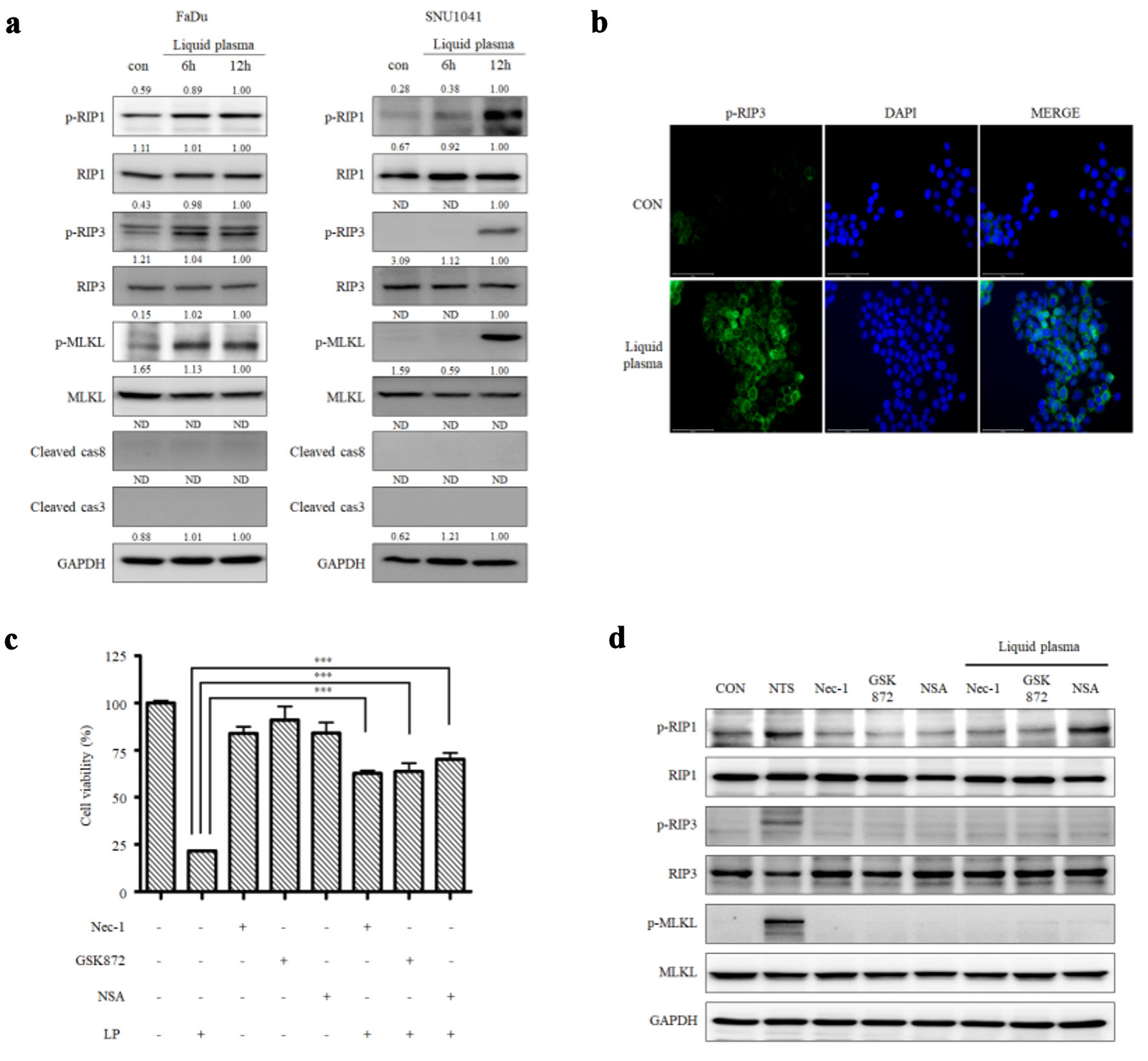
Results: Here, we determined the type of cell death induced by liquid plasma in head and neck cancer (HNC) cells. Our results show that liquid plasma caused necroptosis in HNC cells, and peroxynitrite in the liquid plasma might be involved in the cell death. The expression of inflammation-related molecules, including nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), interleukin (IL)-6, and mitochondrial antiviral signaling proteins, were detected in HNC cells, and treatment of HNC cells with liquid plasma decreased their expression.
Conclusions: These results suggest that liquid plasma could be used to treat HNC by inducing necroptosis without inflammatory responses. In this study, we demonstrated that liquid plasma treatment may kill HNC cells without causing necroptosis-induced inflammation and inflammation-mediated diseases.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









