Comprehensive Investigation of a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant Gene Zeste White 10 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2514Keywords:
Hepatocellular carcinoma, Zeste white 10, Tyrosine kinase inhibitor, Resistance, Nucleocytoplasmic transportAbstract
Background: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are first-line therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but the drug resistance restricts the long-term clinical outcomes. This study aimed to investigate the expression patterns and possible clinical significance of a TKI-resistant gene zeste white 10 (ZW10) in HCC.
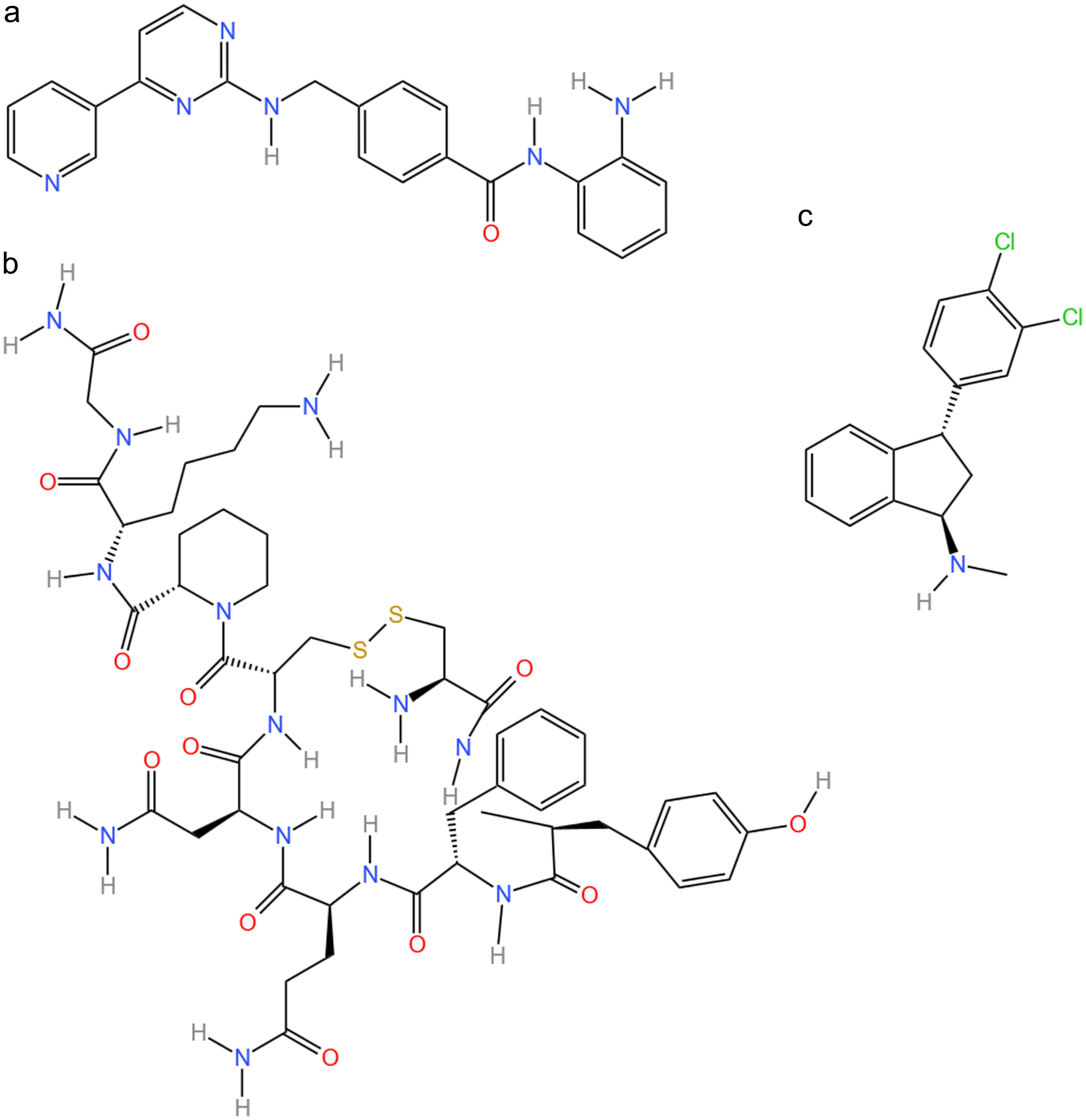
Methods: Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) screening was conducted to obtain TKI-resistant genes. Pan-cancer analysis was employed to analyze the expression landscape of the critical TKI-resistant gene ZW10. Transcriptional expression data for ZW10 were obtained from 76 centers, including 3,312 HCC samples and 2,703 noncancerous tissues. A summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve was built to evaluate ZW10 expression characteristics in HCC. Unpaired two-sample Wilcoxon method was conducted to analyze ZW10 expression levels in HCC of various etiologies. Univariate Cox method was employed to assess the prognostic value of ZW10. Moreover, the gene function within HCC cell lines, the TKI treatment responses, key pathways, and tumor microenvironment of ZW10 were bioinformatically investigated. Drug prediction and molecular docking techniques were used to explore the potency of ZW10 as a novel therapeutic target.
Results: The abundance of small guide RNA (sgRNA) corresponding to ZW10 gene was decreased in the whole genome CRISPR knockout library (LogFC = -1.19), indicating that ZW10 may participate in TKI resistance. The differential expression landscape of ZW10 was found in various malignancies including HCC, which was associated with poorer prognosis. Pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) of ZW10 mRNA expression was 0.47 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.32 - 0.63), the area under SROC was 0.76 (95% CI: 0.72 - 0.79), the sensitivity was 0.63 (95% CI: 0.53 - 0.72), and the specificity was 0.77 (95% CI: 0.67 - 0.84). ZW10 was investigated significant for the growth of HCC cells. Nucleocytoplasmic transport was the possible pathway that ZW10 involved. High level of ZW10 was reversely associated with TKI responses and the abundance of immune cell infiltration. Mocetinostat and capecitabine were predicted to be the potential inhibitors targeting ZW10 with a minimum binding energy of -8.2 and -7.1 kcal/mol, respectively.
Conclusions: ZW10 is considered a TKI-resistant and tumor-supportive gene, which is also a promising novel prognostic biomarker for HCC or a therapeutic target for overcoming TKI resistance.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









