Increased Sirtuin 6 Activity in Tumor Cells Can Prompt CD4-Positive T-Cell Differentiation Into Regulatory T Cells and Impede Immune Surveillance in the Microenvironment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2547Keywords:
Tregs, Immune surveillance, Tumor microenvironment, Sirt6, ADO, PD-1/PD-L1, IFN-γAbstract
Background: Sirtuin 6 (Sirt6) is expressed at increased levels in many tumors and may be involved in immunoregulation. The present study investigated how Sirt6 in tumor cells affects immune surveillance.
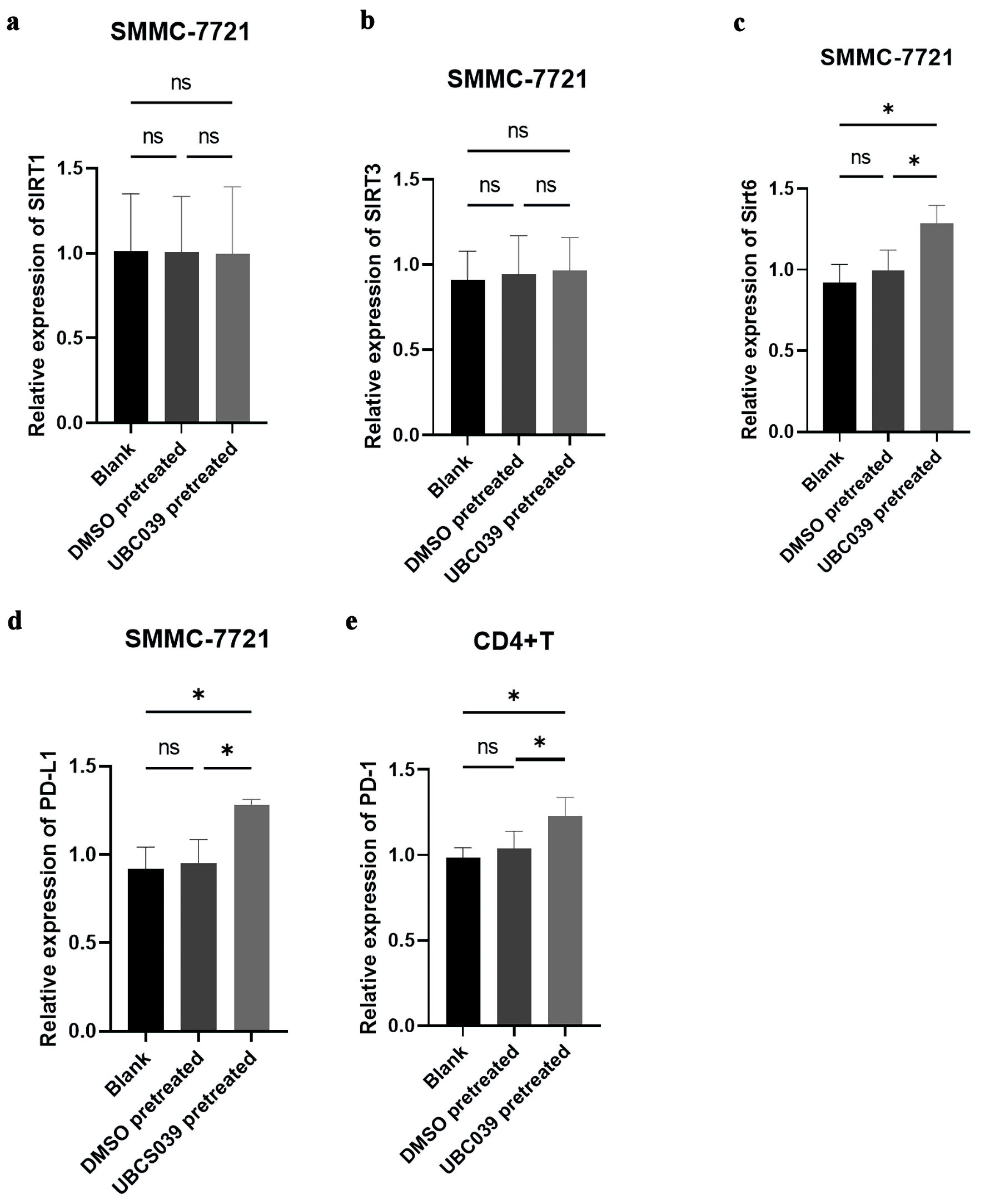
Methods: The human tumor cell lines A2780, HeLa, Huh7, MBA-MD-231, SMMC-7721 and SW480 were incubated with UBCS039, a target-selective activator of Sirt6, to stimulate Sirt6 activity. These cells, following washing to remove residual UBCS039, were cultured with human naive CD4+ T cells in the Transwell to observe the T cell differentiation. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) among CD4+ T cells and the levels of various cytokines and adenosine (ADO), an immunosuppressive metabolite, in the culture medium, were measured via flow cytometry. The treated tumor cells were examined via transcriptomic analysis. The transcriptomic results, as well as programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1), programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and Sirt6 expression in tumor cells and CD4+ T cells were verified via real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Results: Following culture with UBSC039-pretreated tumor cells, the proportion of Tregs among CD4+ T cells was significantly increased. PD-L1 and Sirt6 expressions in UBS039-pretreated tumor cells and PD-1 expression in cocultured CD4+ T cells were also increased. Moreover, the ADO level increased, and the interleukin (IL)-10, interferon (IFN)-α2, IFN-γ and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) levels decreased in the coculture medium. Transcriptomic analysis revealed significant downregulation of the antitumor genes BASP1, CPS1, GNG11, MFAP5, NNMT and SMOC1, upregulation of the tumor-promoting genes FOXA2, GSTP1, RASEF and ZNF844, and activation of adherens junctions, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-signaling and the circadian rhythm pathway in UBCS039-pretreated SMMC-7721 cells. The above results were verified in all six cell lines.
Conclusions: The present study suggested that increased Sirt6 expression and activity in tumor cells can suppress immune surveillance by increasing Treg, ADO, PD-1 and PD-L1 levels, decreasing IFN-γ production, and altering tumor-promoting and antitumor gene expression in the microenvironment.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









