Targeting the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Pathway Suppresses Y-Box Binding Protein 1 Expression and Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Progression
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2640Keywords:
Colorectal cancer, YBX1, PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, BKM120, HypoxiaAbstract
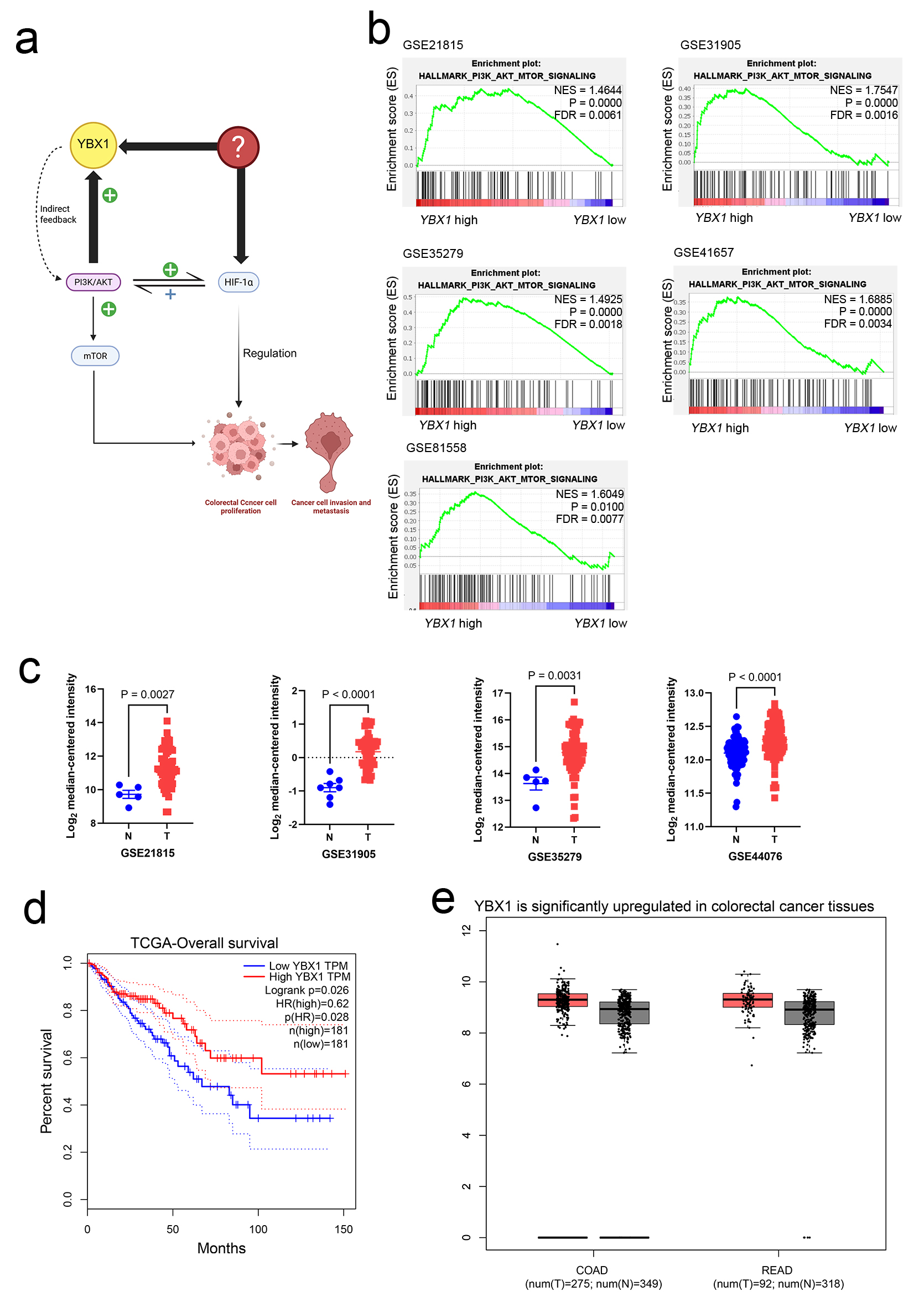
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most prevalent and lethal malignancies worldwide, often characterized by the aberrant activation of multiple signaling pathways. Y-box binding protein 1 (YBX1), a multifunctional regulator of transcription and translation, has been identified as an oncogenic factor in various solid tumors. However, its expression profile and mechanistic role in CRC remain largely unclear.
Methods: In this study, integrative bioinformatic analyses were conducted on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets to assess YBX1 expression and its correlation with CRC progression. Functional assays, including cell proliferation and migration assays, were performed to investigate the role of YBX1 in CRC cells. The impact of YBX1 on the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) signaling pathway was evaluated, and the effects of the PI3K inhibitor buparlisib (BKM120) on YBX1-driven cellular phenotypes were also tested.
Results: YBX1 was found to be significantly upregulated in CRC tissues and was closely associated with the activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. YBX1 overexpression promoted CRC cell proliferation and migration, whereas knockdown of YBX1 inhibited these processes. Mechanistically, YBX1 was shown to enhance PI3K/AKT signaling activity, promoting malignant phenotypes in CRC. Treatment with BKM120 partially reversed these effects. Additionally, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) identified enrichment of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-related pathways in YBX1-high CRC samples.
Conclusions: This study highlights the oncogenic role of YBX1 in CRC and reveals a potential YBX1-PI3K/AKT regulatory axis that may serve as a promising therapeutic target. The findings suggest that targeting this axis could provide a novel strategy for CRC treatment, especially under hypoxic or microenvironmental stress conditions.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









