Actionable Mutations and Survival Rates in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2531Keywords:
Lung cancer, Actionable mutations, Next-generation sequencing, Non-small cell lung cancer, JordanAbstract
Background: In Jordan, lung cancer ranks as the second most common tumor, and there is an urgent need to explore the genetic landscape of lung cancer. This study aimed to identify the actionable mutations in lung cancer samples in Jordanians by targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) and to investigate the correlations with clinical and pathological parameters.
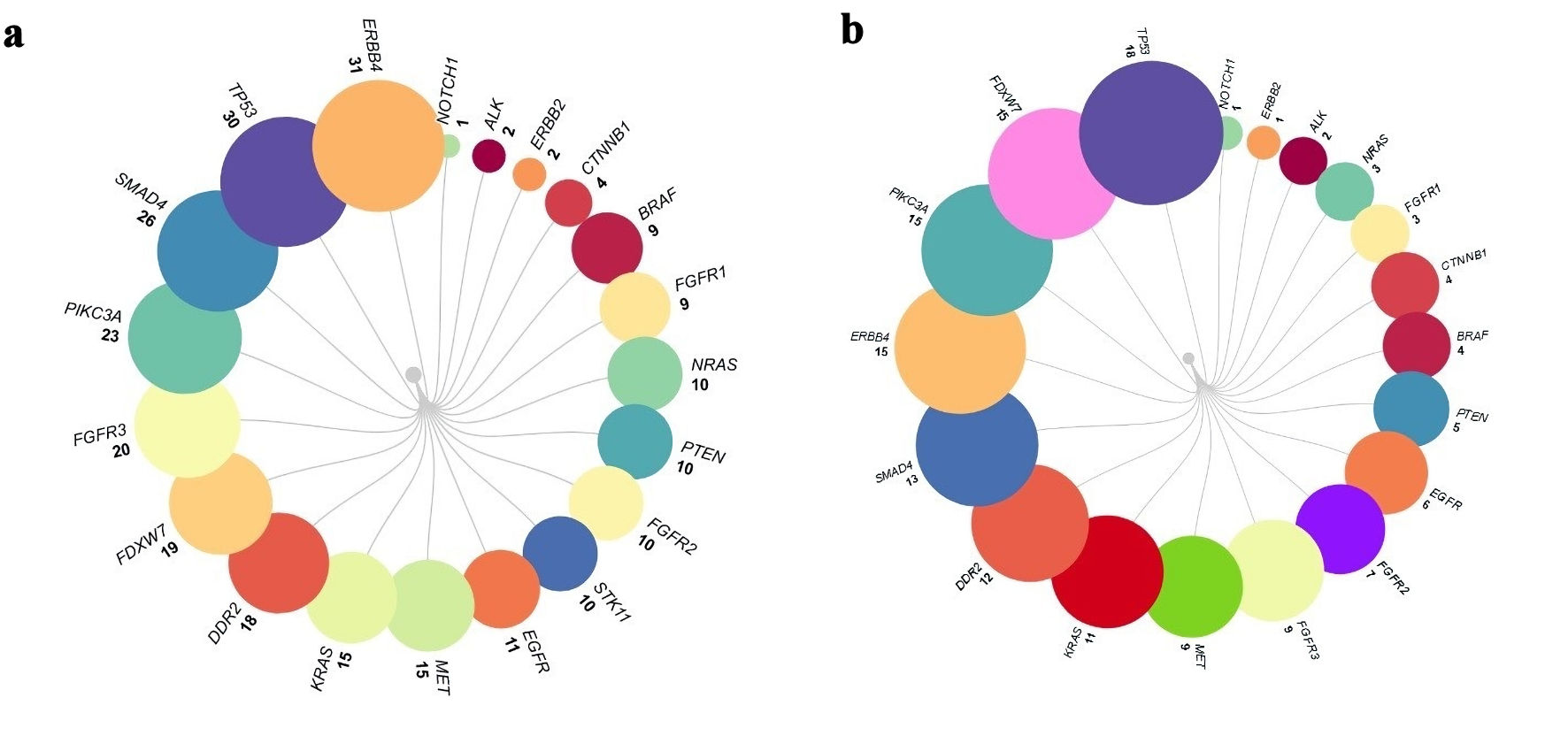
Methods: Totally, 121samples were prepared for NGS by DNA extractions from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) blocks, followed by library preparation using the AmpliSeq Colon and Lung panel, which covers mutational hot spot regions for 22 cancer genes.
Results: Amongst 121 patients, 88% of those treated for non-small lung carcinoma were successfully analyzed; 35 (29%) carried one mutation or more in actionable genes (KRAS, EGFR, ALK, BRAF, and MET). There are no significant differences between actionable mutation carriers and non-carriers concerning histological tumor type, tumor stage, metastasis, smoking habits, and gender. However, the analysis of survival probabilities revealed lower survival times for females compared to males, as well as for those patients who had metastasis events, smoking, or relapse after treatment.
Conclusions: The type and rates of mutations detected for lung tumors in Jordan are relatively similar to those found in other populations previously studied, although some differences exist. However, lung tumors in Jordan require new customized treatment prescriptions based on prior genetic studies, as part of the hoped-for trend toward precision medicine.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









