High CDCP1 Expression Reflects Immune and Stromal Remodeling and Oncogenic Signaling in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2682Keywords:
Biomarker, CDCP1, Genomic instability, Immunosuppression, Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomaAbstract
Background: CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1) is implicated in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) prognosis, but its relationship to the tumor microenvironment (TME) and oncogenic signaling remains incompletely defined. We hypothesized that CDCP1 expression is associated with hallmark cancer signaling pathways and transcriptionally inferred TME remodeling in PDAC.
Methods: We analyzed transcriptomic and clinical data from 214 PDAC cases (The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), n = 145; GSE62452, n = 69). Patients were stratified into high CDCP1 and low CDCP1 groups based on the top tertile of expression. Immune and stromal components of the TME were quantified using the xCell algorithm. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) with Hallmark gene sets was used for pathway enrichment.
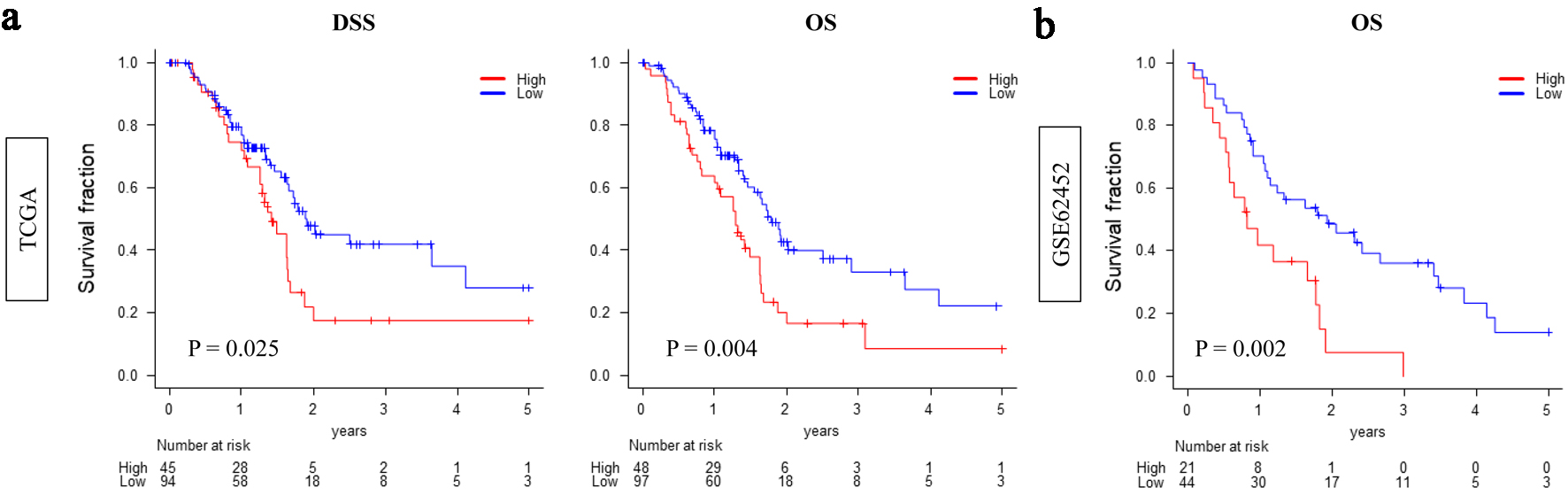
Results: High CDCP1 expression was significantly associated with reduced infiltration of CD8+ T cells, adipocytes, and fibroblasts, suggesting an immune-excluded and stromally depleted TME. It also correlated with increased homologous recombination deficiency scores, mutation burden, and single-nucleotide variants. CDCP1 expression correlated with CDKN2A mutation but was only weakly associated with KRAS, TP53, and SMAD4 alterations. GSEA showed consistent enrichment of proliferative (E2F, MYC, G2M, p53) and protumorigenic (transforming growth factor-β, hypoxia, glycolysis) pathways in high CDCP1 tumors across both datasets.
Conclusion: CDCP1 defines a transcriptionally distinct PDAC subtype characterized by immune evasion, stromal depletion, and genomic instability. These findings highlight CDCP1 as a potential therapeutic target and biomarker reflecting interplay between oncogenic signaling and the TME.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









