Development and Validation of KN-DIOC: A Novel Preoperative Diagnostic Index Using Ultrasound, Complete Blood Count, and Cancer Antigen 125 for Ovarian Cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2595Keywords:
Ovarian cancer, Predictive model, Complete blood count, Tumor marker, UltrasoundAbstract
Background: Ovarian cancer, particularly epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), is one of the deadliest gynecological malignancies due to nonspecific early symptoms and late diagnosis. Current diagnostic tools, while useful, often do not account for regional variations in disease presentation, particularly in Asian populations. This study aimed to develop and validate a new preoperative diagnostic index tailored to the Thai population by integrating complete blood count (CBC), tumor markers, and ultrasound features.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included patients with pathologic pelvic or adnexal masses scheduled for surgery at Vajira Hospital from April 2022 to October 2024. Clinical data, CBC, cancer antigen 125 (CA125) levels, and ultrasound findings were analyzed to develop and validate a diagnostic index (KMUTT-NMU Diagnostic Index for Ovarian Cancer (KN-DIOC)). The model’s performance was compared against established indices like Risk of Malignancy Index (RMI), Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm (ROMA), and Rajavithi-Ovarian Cancer Predictive Score (R-OPS) through multivariate logistic regression, focusing on key predictors.
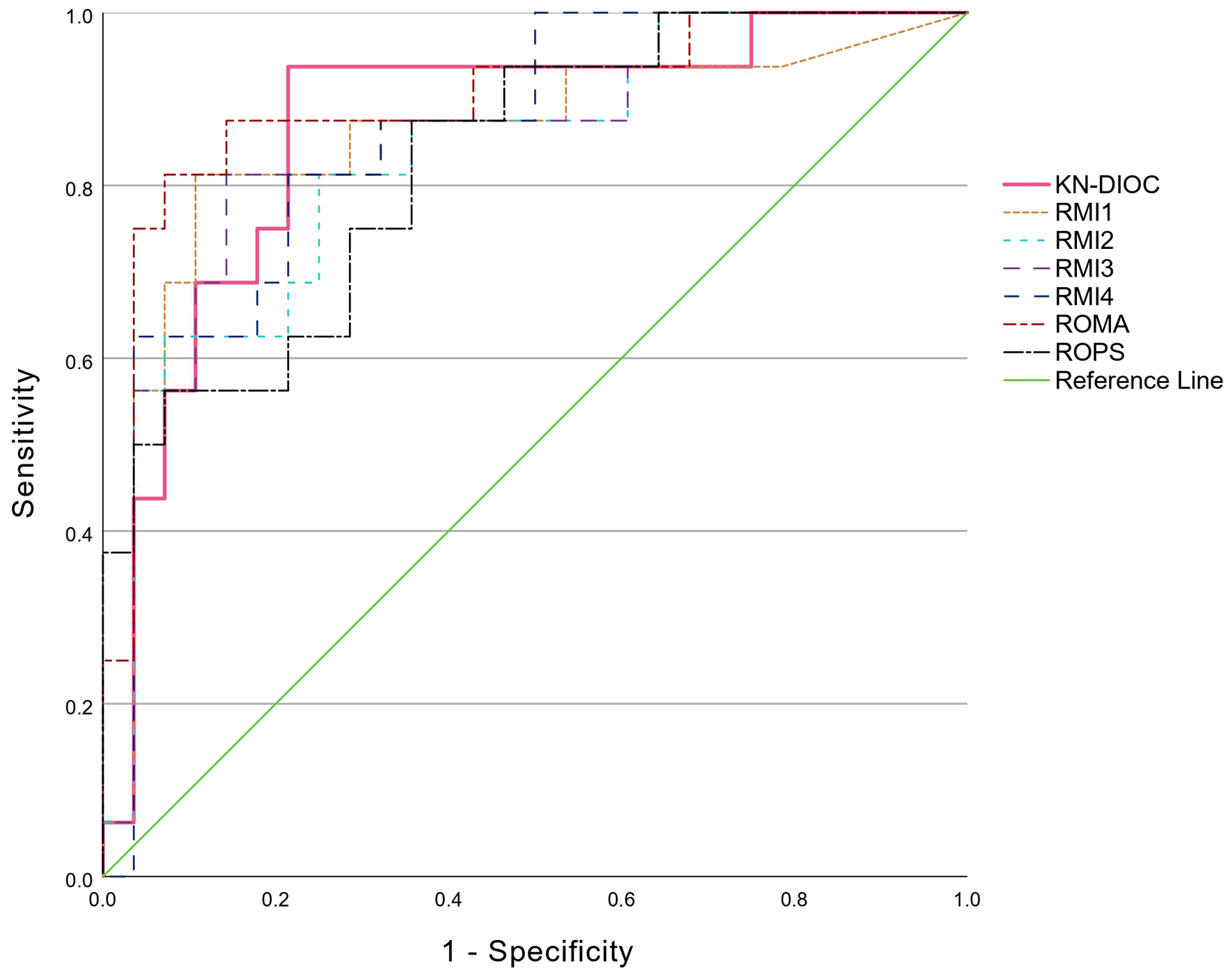
Results: The study comprised 195 patients divided into 151 for the development dataset and 44 for the validation dataset. The KN-DIOC showed high discriminative ability with an area under curve (AUC) of 0.866, indicating very good capability in differentiating between benign and malignant ovarian masses. The index achieved a sensitivity of 93.75% and a specificity of 78.57%, demonstrating superior performance to traditional diagnostic tools, especially in the validation dataset.
Conclusion: The novel diagnostic index (KN-DIOC), incorporating CBC, ultrasound features, and tumor markers, provides a robust tool for preoperative assessment of ovarian tumors in Thai patients. It offers significant improvements in sensitivity and specificity over existing models, suggesting its potential for broader application in similar settings. This index supports enhanced decision-making in gynecological oncology, potentially leading to better patient outcomes through timely and accurate diagnosis.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









