Angiogenesis Is Associated With Aggressive Biology That Counterbalances With Tumor Immunogenicity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2009Keywords:
Hepatocellular carcinoma, Angiogenesis, ImmunogenicityAbstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an arterialized tumor; thus, anti-angiogenesis targeted therapy is in clinical practice. Herein, we hypothesized that HCC with high angiogenesis is biologically aggressive with worse survival.
Methods: Angiogenesis score (AS) was derived from the Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) Hallmark Angiogenesis Gene Set, and median was used to divide high versus low groups. Transcriptome of HCC patients of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA, n = 386) and GSE76427 (n = 115) cohorts were analyzed.
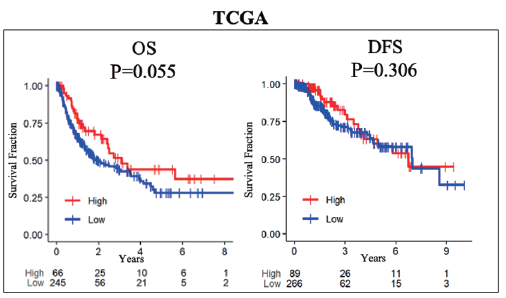
Results: High AS correlated with angiogenesis-related gene expressions. Both microvascular and lymphatic endothelial cell infiltrations were higher in high angiogenesis HCC. Surprisingly, no survival difference was seen with varying levels of angiogenesis. High angiogenesis significantly enriched tumor aggravating signaling pathways: glycolysis, Notch, Hedgehog, KRAS, epithelial mesenchymal transition, and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) in Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA), but also infiltrated less CD8+ T cells and T-helper 1 cells, and higher M1 macrophages and conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) with elevated cytolytic activity score in both cohorts. In agreement, immune response-related gene sets: inflammatory response, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) signaling, allograft rejection, interferon-alpha, and interferon-gamma were all enriched to high angiogenesis HCC. Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1), programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), programmed death ligand 2 (PD-L2), and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) were higher in high angiogenesis HCC in TCGA, but not in GSE76427 cohort.
Conclusions: Angiogenesis quantified using transcriptome of HCC patients demonstrated that it is associated with aggressive biology but also with tumor immunogenicity and immune response that counterbalance and did not reflect in survival. Given high expression of immune checkpoint molecules, we cannot help but speculate that immunotherapy may be useful for high angiogenesis HCC patients.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









