LINC01121 Is Associated With Prognosis and Facilitates the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2629Keywords:
LINC01121, Colorectal cancer, Biomarkers, PrognosisAbstract
Background: The role of LINC01121 in the pathogenesis and prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) remains unknown. This study aimed to explore the function of LINC01121 in CRC development.
Methods: Transcriptome expression data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database were utilized to investigate the relationship between LINC01121 and CRC prognosis through survival analysis. Samples from CRC patients and adjacent tissues were collected and analyzed to assess the expression differences between tumor and adjacent tissues. Functional assays such as Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8), EdU, scratch test, and Transwell assay were employed to determine the oncogenic role of LINC01121 in CRC cells. Additionally, gene enrichment analyses and immune infiltration analyses were conducted with R package.
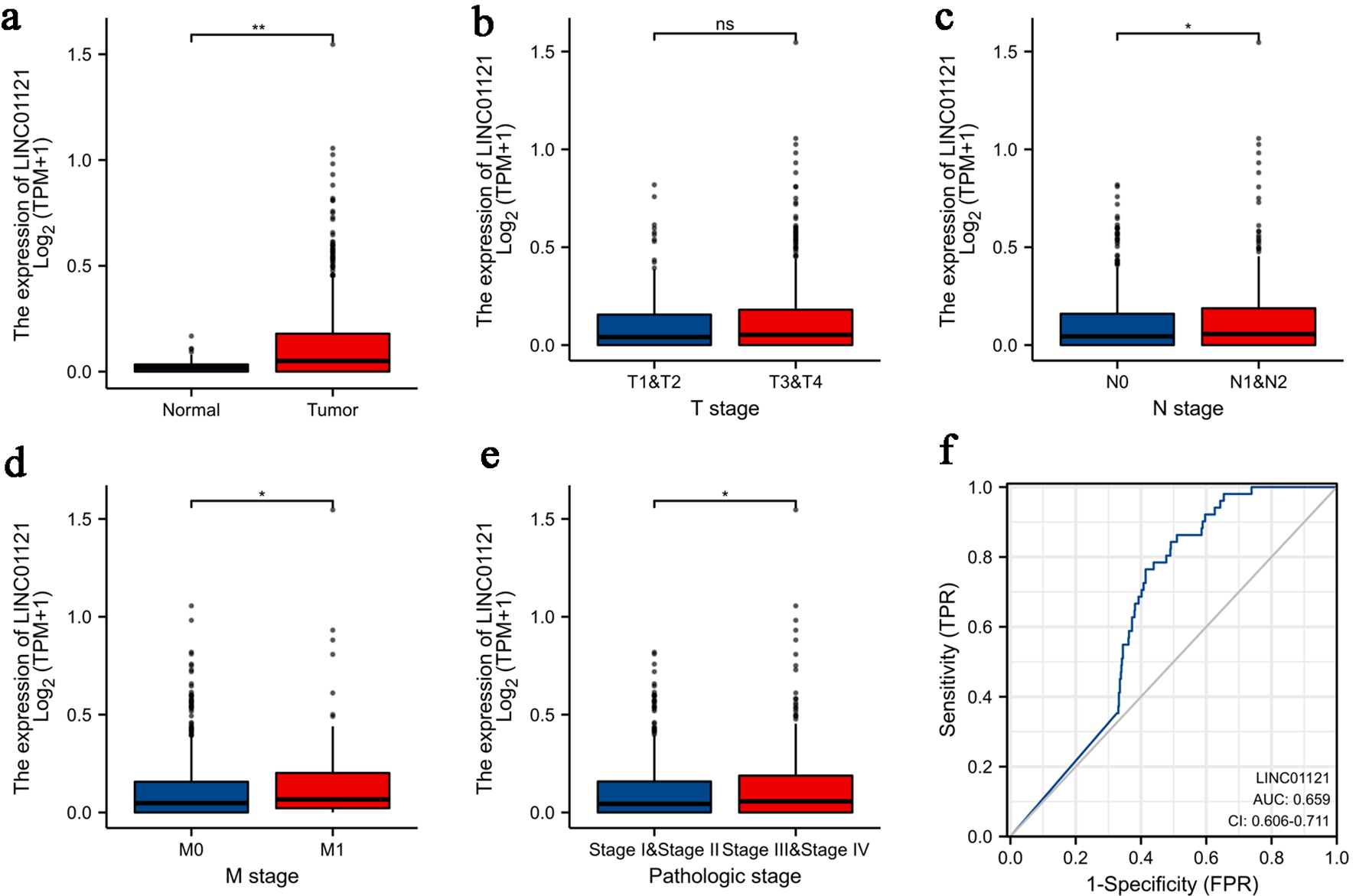
Results: The LINC01121 level was obviously higher in CRC tissues. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve suggests that LINC01121 has significant diagnostic capabilities (area under the curve (AUC) = 0.659). High expression of LINC01121 predicted poor overall survival (OS) (P = 0.022), progression-free interval (PFI) (P = 0.007), and disease-specific survival (DSS) (P = 0.006). Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) demonstrated that LINC01121-associated CRC encompasses various crucial pathways linked to tumorigenesis. The immune infiltration analyses revealed that LINC01121 may be involved in immune suppression. In vitro experiments demonstrated that LINC01121 facilitated the proliferation, migration, and invasion of CRC cells.
Conclusion: LINC01121 exhibits elevated expression in CRC and correlates with unfavorable prognosis and reduced immune infiltration in CRC patients. These findings suggest that LINC01121 may serve as a potential marker for the diagnosis and prognosis of CRC.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









