Co-expression of HER2/EGFRvIII/CD44 and Claudin 18.2/CD109 as Novel Prognostic Indicators in Stomach Adenocarcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2552Keywords:
Stomach cancer, Prognosis, EGFRvIII, CD44, Claudin 18.2, CD109Abstract
Background: The heterogenous expression of human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) family members may contribute to poor response to current therapies with HER inhibitors in cancer. This study aimed to explore the co-expression and prognostic significance of HER family members with epidermal growth factor receptor variant III (EGFRvIII), cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44), cluster of differentiation 109 (CD109), and claudin 18.2 (CLDN18.2) in patients with stomach cancer.
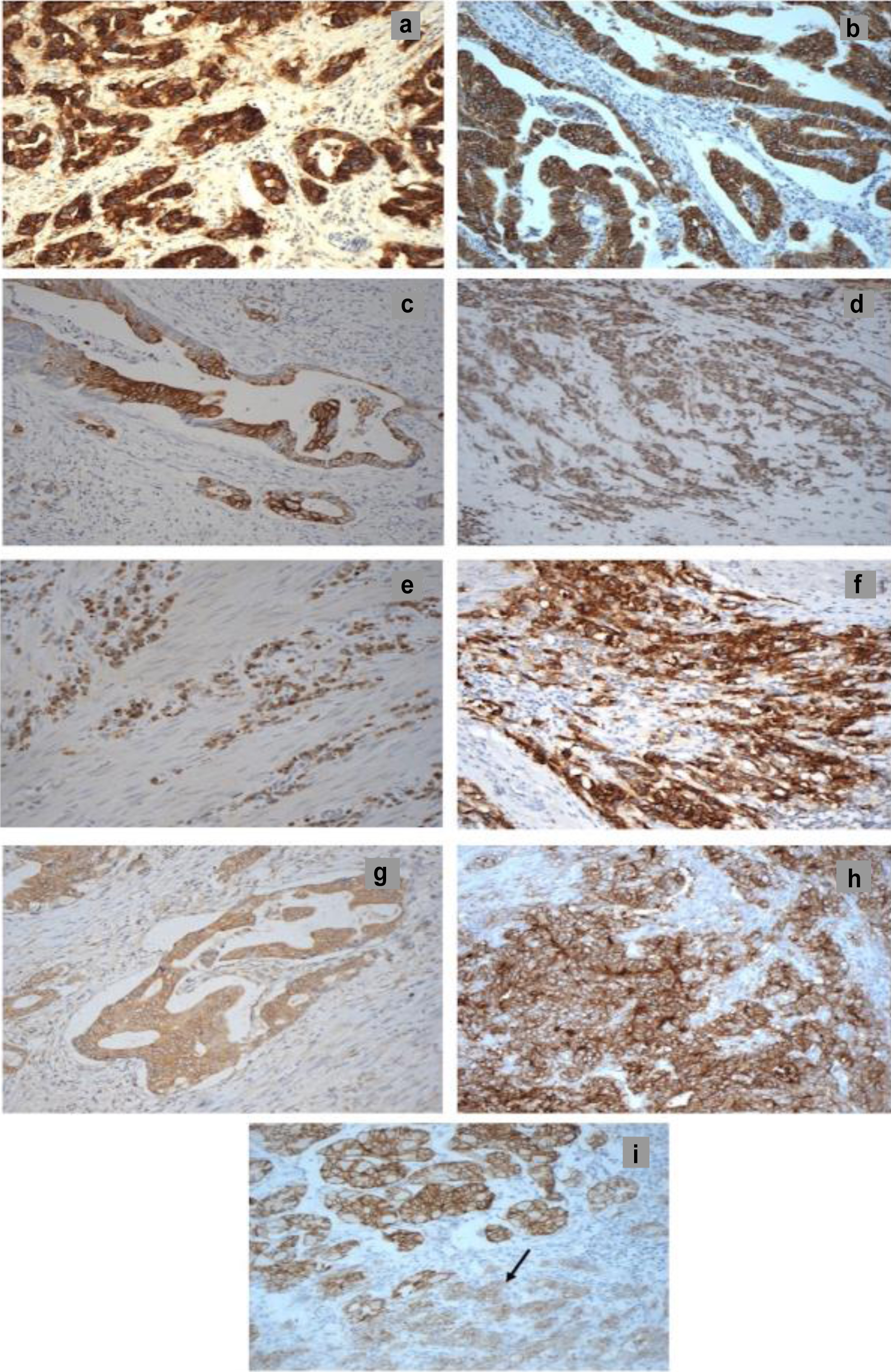
Methods: The relative expression and prognostic significance of these biomarkers at different cut-off values were determined in 78 patients with stomach adenocarcinoma by immunohistochemistry.
Results: Of the 78 cases, positive tumor staining was present for wild-type EGFR (13%), HER2 (82%), HER3 (9%), HER4 (33%), EGFRvIII (33%), CD44 (41%), CD109 (60%), and CLDN18.2 (40%). Furthermore, the expression of HER2 was accompanied with the co-expression of EGFR (9%), HER3 (8%), HER4 (27%), EGFRvIII (28%), CD44 (33%), CD109 (49%), and CLDN18.2 (32%). Interestingly, at the cut-off value ≥ 5% of tumor cells with positive staining, the co-expressions of HER2/EGFRvIII, EGFRvIII/CD44, and HER2/EGFRvIII/CD44 were associated with poor overall survival. Moreover, CLDN18.2 immunostaining of intensity of 3+, membranous expression of CD109, the co-expression of CD109/CLDN18.2 and CD109/EGFRvIII/CD44 were also associated with poorer overall survival and a higher risk of poor overall survival. All these remained as independent prognostic factors for survival in multivariate analysis.
Conclusion: This study provides first comprehensive analysis of the novel biomarker combinations that are significantly associated with overall survival. Co-expression of HER2 with EGFRvIII, CD44, and CD109, plus membranous CD109 and high-intensity CLDN18.2, independently predicted poor survival in stomach adenocarcinoma, highlighting their potential as prognostic biomarkers. These biomarker combinations may represent potential therapeutic targets for novel combination therapies, and future studies should investigate their predictive value for the response to therapy.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









