Mechanism of Action of Resveratrol Affecting the Biological Function of Breast Cancer Through the Glycolytic Pathway
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2586Keywords:
Resveratrol, Breast cancer, Glycolysis, Invasion, ApoptosisAbstract
Background: Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) plays a crucial role in the glycolytic pathway and its overexpression has a negative impact on tumor development and prognosis. Resveratrol, a natural polyphenolic compound, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-tumor properties. However, the mechanism by which resveratrol inhibits breast cancer growth, invasion, and metastasis through the PGK1 glycolytic pathway is still not fully understood.
Methods: We used the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) and the Human Protein Atlas database to analyze the expression levels of glycolytic enzymes in different breast tissues and their correlation with the prognosis of breast cancer patients. The effect of resveratrol on the biological functions of breast cancer was studied through wound healing experiments and Transwell migration and invasion experiments. Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), Western blot, and in vivo mouse tumorigenesis experiments were used to explore the possible molecular mechanism of resveratrol inhibiting the occurrence and development of breast cancer.
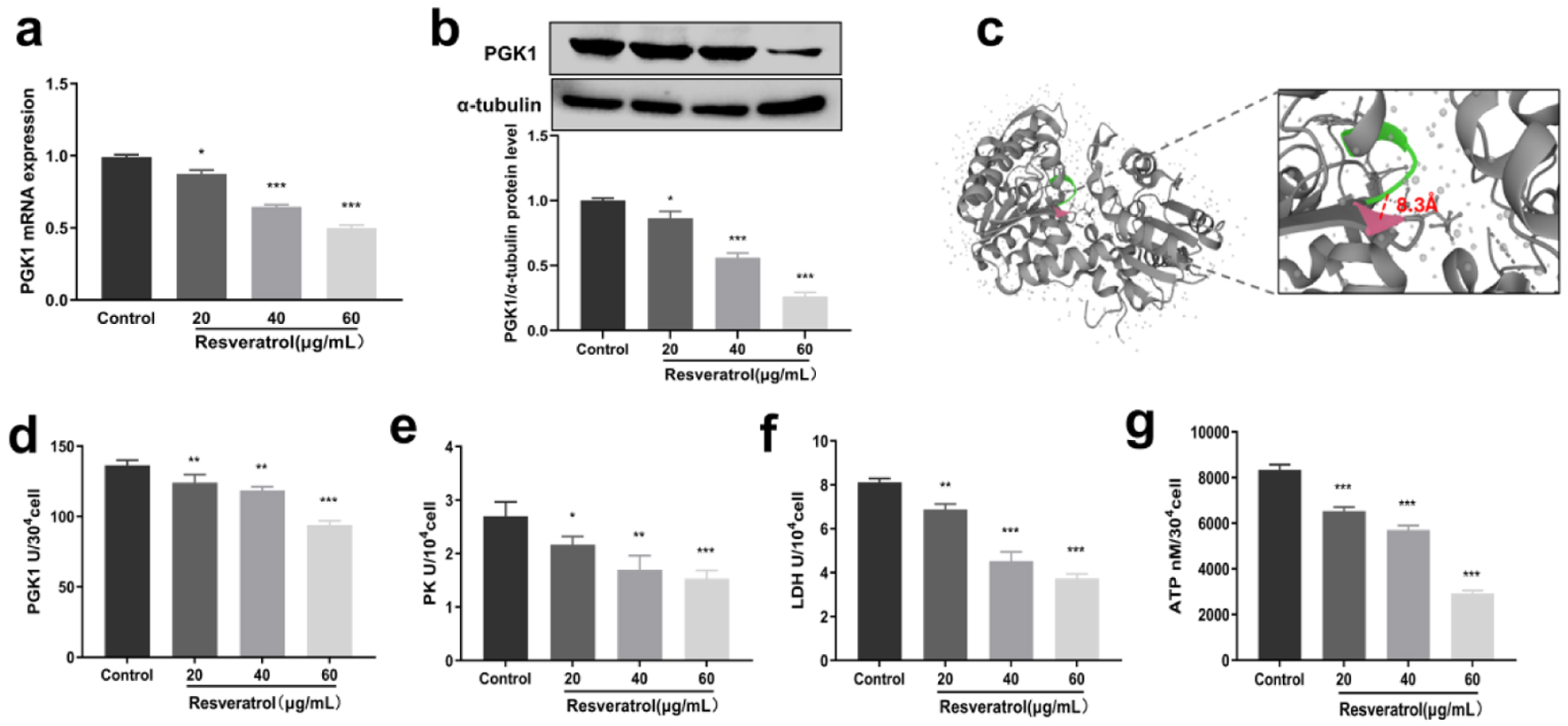
Results: Resveratrol exerted oncogenic effects both in vivo and in vitro. In our study, we provided additional evidence to support the role of resveratrol in breast cancer treatment. Specifically, we found that resveratrol effectively reduced the expression of PGK1 in BT-549 cells. This reduction is achieved by regulating an important transcription factor c-Myc. As a result, the cellular glycolytic pathway is blocked, leading to the inhibition of malignant biological behavior in breast cancer cells.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that targeting the PGK1 glycolytic pathway could be a promising approach for resveratrol-based treatment of breast cancer.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









