Effect of Whey Protein Supplementation on Postoperative Outcomes After Gynecological Cancer Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon1990Keywords:
Whey protein supplementation, Gynecological cancer surgery, Postoperative outcomes, Randomized controlled trialAbstract
Background: Whey protein’s biochemical properties make it an ideal nutritional supplement for patients with cancer, especially in perioperative care. Thus, the present study aims to assess the efficacy of whey protein supplementation (WPS) compared to standard care in enhancing postoperative outcomes for patients undergoing comprehensive surgical staging for gynecological cancer.
Methods: In an open-label, randomized controlled trial conducted at Rajavithi Hospital between November 28, 2023 and July 8, 2024, 61 patients scheduled for comprehensive surgical staging were enrolled. Participants were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either the WPS group (n = 30) or the control group (n = 31). The WPS group received isolated whey protein powder (20 g of protein per serving), administered at 6 pm before surgery and 6 am on the first postoperative day. The control group received standard postoperative care. The primary endpoint was the length of hospital stay (LOHS), with secondary outcomes including gastrointestinal function recovery, postoperative analgesic use, complications, and potential WPS-related adverse events such as transaminitis, acute kidney injury, and electrolyte imbalances.
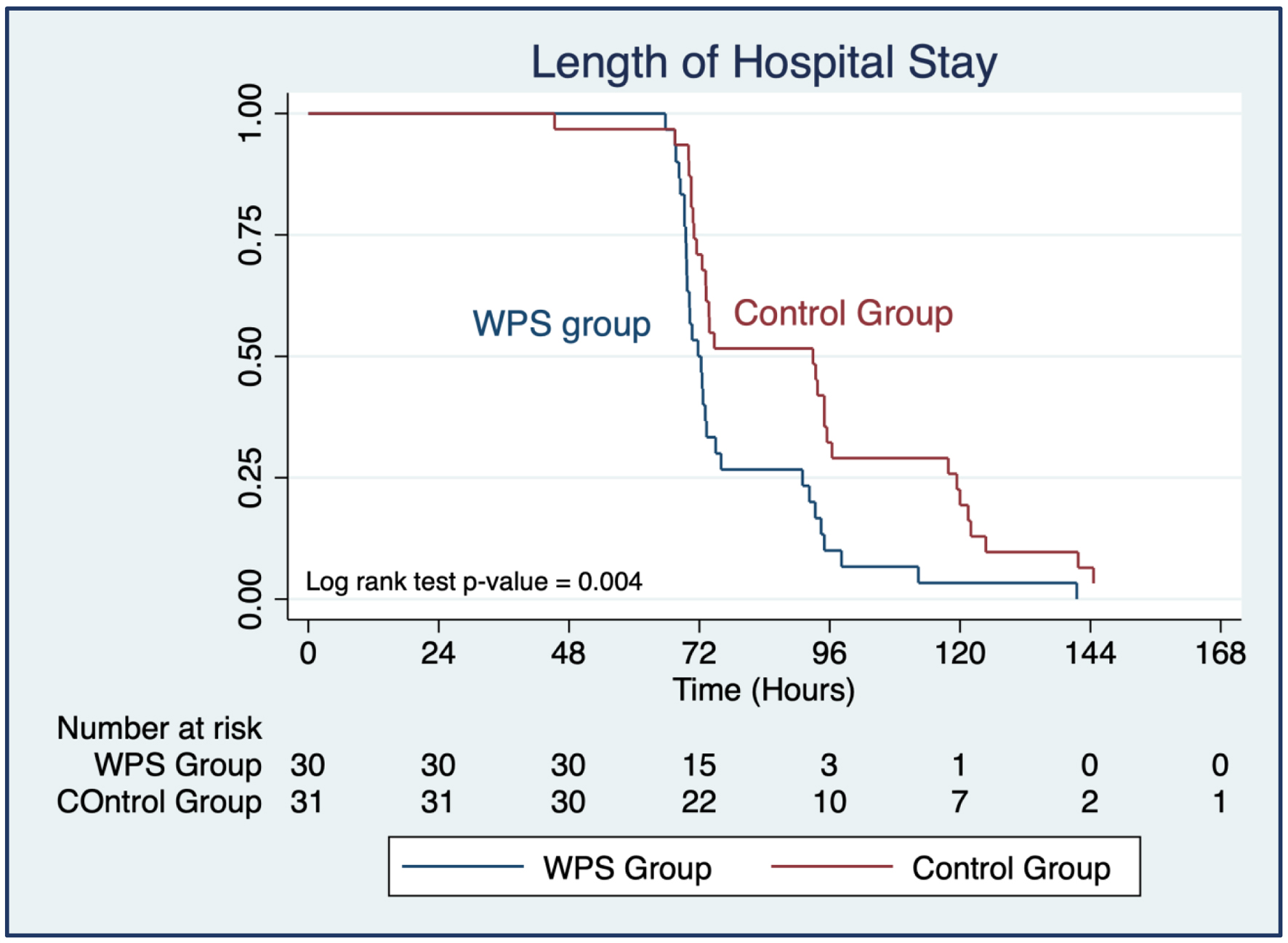
Results: The WPS group had a significantly shorter LOHS than the control group (79.0 ± 6.7 vs. 93.3 ± 28.4 h, P = 0.021). Additionally, the WPS group demonstrated significant improvements in gastrointestinal function, with shorter times to first flatus (P < 0.001), first defecation (P = 0.013), and first ambulation (P = 0.043). No significant differences were observed between the groups regarding postoperative analgesic use or complications, including fever, nausea/vomiting, wound infection, and readmission (P > 0.05). Furthermore, no WPS-related adverse events were reported.
Conclusion: The use of WPS in the perioperative operative management of gynecological cancer surgery yields promising results by significantly reducing the LOHS and accelerating the recovery of gastrointestinal function while maintaining a favorable safety profile.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









