Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Versus Anti-Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in PD-L1-Negative Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon2520Keywords:
Non-small cell lung cancer, PD-L1 negative, Anti-PD-1, Anti-PD-L1, ImmunotherapyAbstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) which target programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) receptor or its ligand (PD-L1) are used extensively in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In this article, we compared the relative efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors and PD-L1 inhibitors in PD-L1-negative advanced NSCLC.
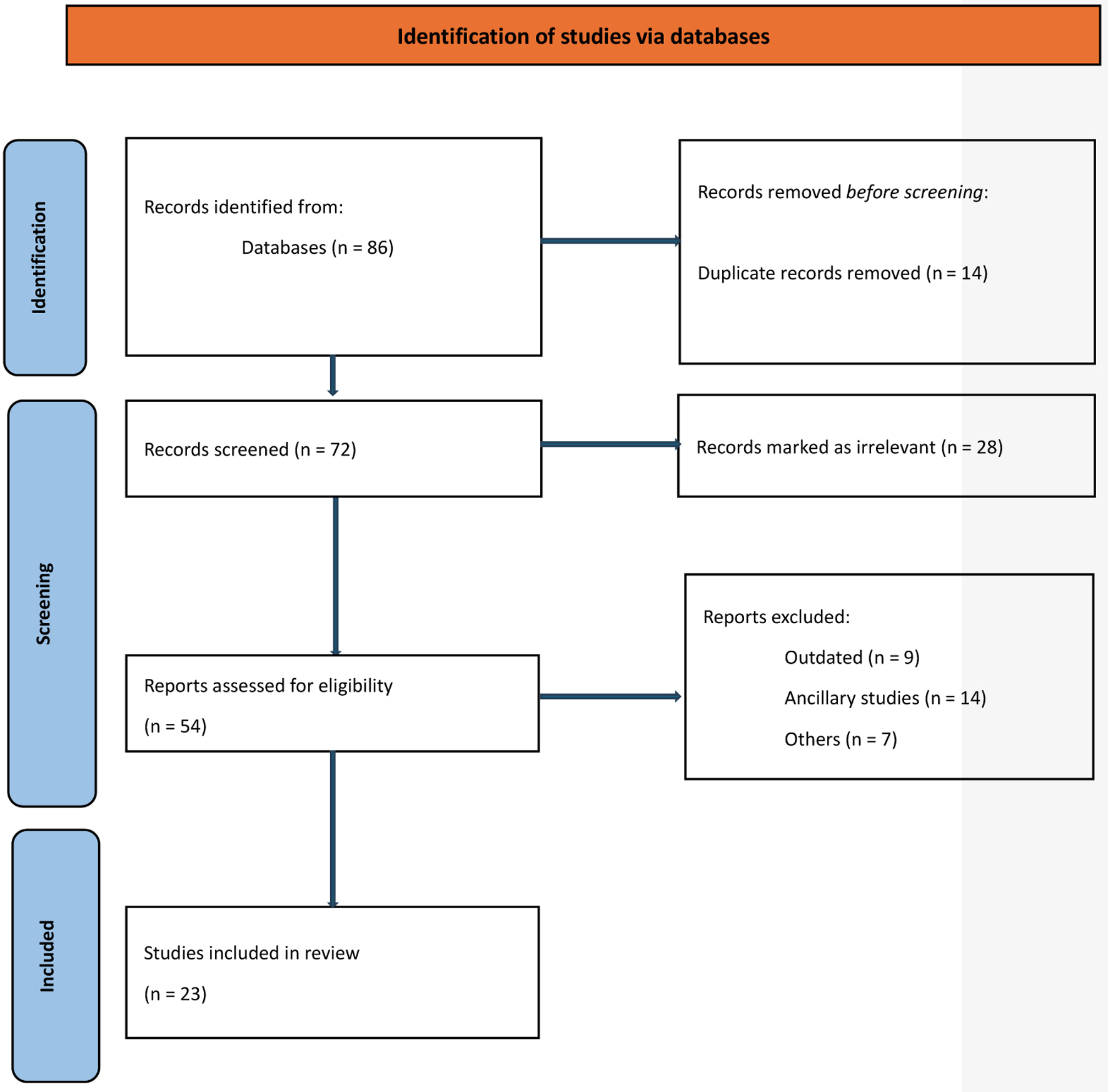
Methods: We searched MEDLINE (host: PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar) for randomized trials for advanced NSCLC in which ICIs (anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1) were used where outcome data were reported based on PD-L1 testing, including the subset of PD-L1-negative patients. We extracted hazard ratios (HRs) and related 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and/or P values for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) for the PD-L1-negative subgroup of each included trial. We then pooled data using a random effects meta-analysis and compared anti-PD-1 to anti-PD-L1 inhibitors. Variations in effect size were examined using subgroup analyses.
Results: Twenty-three trials were included in the meta-analysis. PD-L1 testing was performed in all participants. A total of 4,548 PD-L1-negative patients were included in the analysis, representing 33% of all participants in the included clinical trials. Overall, the addition of anti-PD-1 was associated with better OS in PD-L1-negative advanced NSCLC patients (HR: 0.75, 95% CI: 0.67 - 0.83, P < 0.01), while the addition of anti-PD-L1 inhibitors showed no improvement in OS (HR: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.78 - 1.05, P = 0.18). Compared to anti-PD-L1 agents, anti-PD-1 resulted in better OS in PD-L1-negative patients (HR: 0.83, 95% CI: 0.67 - 0.99, P = 0.01). The differential benefit of anti-PD-1 over anti-PD-L1 was of larger magnitude when checkpoint inhibitors were used in the first-line setting (pairwise comparison HR: 0.79, 95% CI: 0.66 - 0.93, P = 0.01), while there was no difference for later lines of therapy (pairwise comparison 1.13; 95% CI: 0.82 - 1.55, P = 0.45). These differences in OS were not observed when pooling PFS data.
Conclusions: Compared to checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD-L1, those targeting PD-1 are associated with better OS in PD-L1-negative advanced NSCLC, a finding influenced by trials performed in the first-line sitting. These data should be validated using real-world studies.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









