Figures
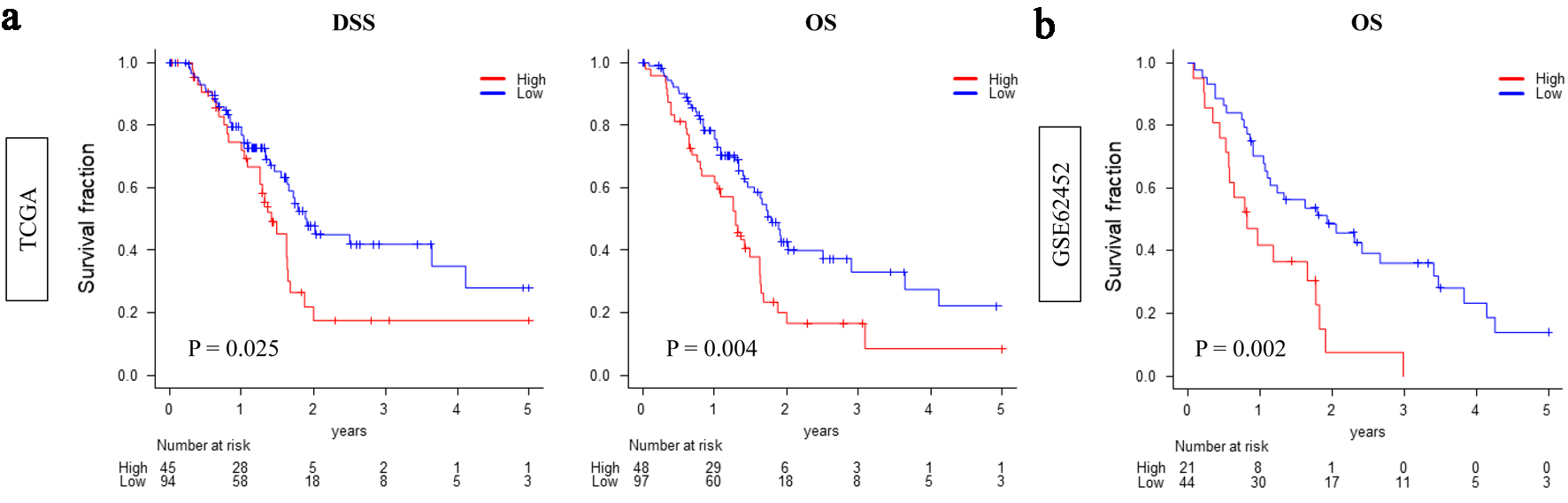
Figure 1. High CDCP1 expression is associated with poor survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Kaplan-Meier survival curves comparing overall survival between high CDCP1 and low CDCP1 groups in the TCGA and GSE62452 cohorts. Survival endpoints include disease-specific survival (DSS) and overall survival (OS) in TCGA (a) and OS in GSE62452 (b). Log-rank test was used to evaluate statistical significance.
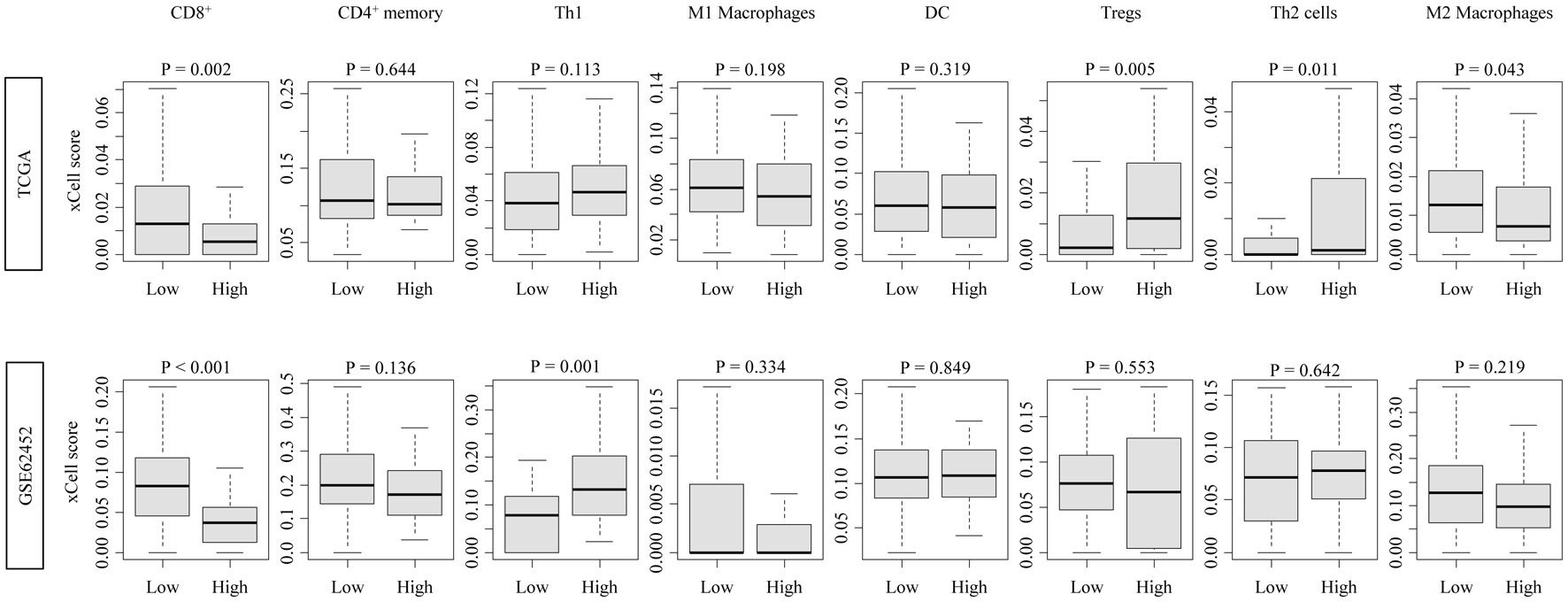
Figure 2. Immune cell infiltration profiles associated with CDCP1 expression in PDAC. Boxplots showing xCell-inferred infiltration scores of CD8+ T cells, CD4+ memory T cells, Th1 cells, Th2 cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), dendritic cells (DCs), and M1/M2 macrophages in high CDCP1 and low CDCP1 groups in the TCGA and GSE62452 cohorts.
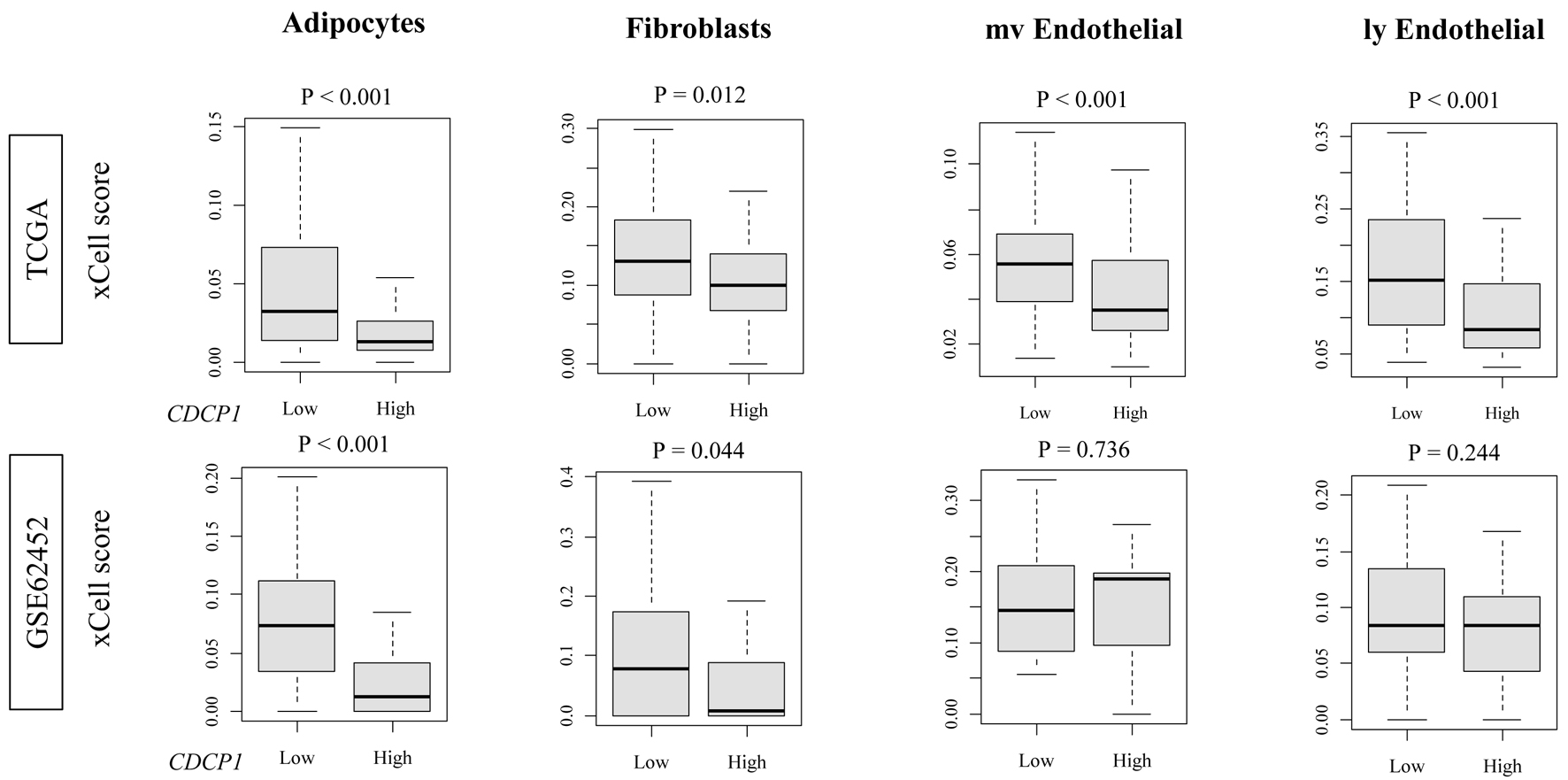
Figure 3. Stromal and endothelial cell fractions in high CDCP1 versus low CDCP1 PDAC tumors. xCell scores comparing infiltration of adipocytes, fibroblasts, microvascular endothelial cells (mvECs), and lymphatic endothelial cells (lyECs) between high CDCP1 and low CDCP1 tumors in the TCGA and GSE62452 cohorts.
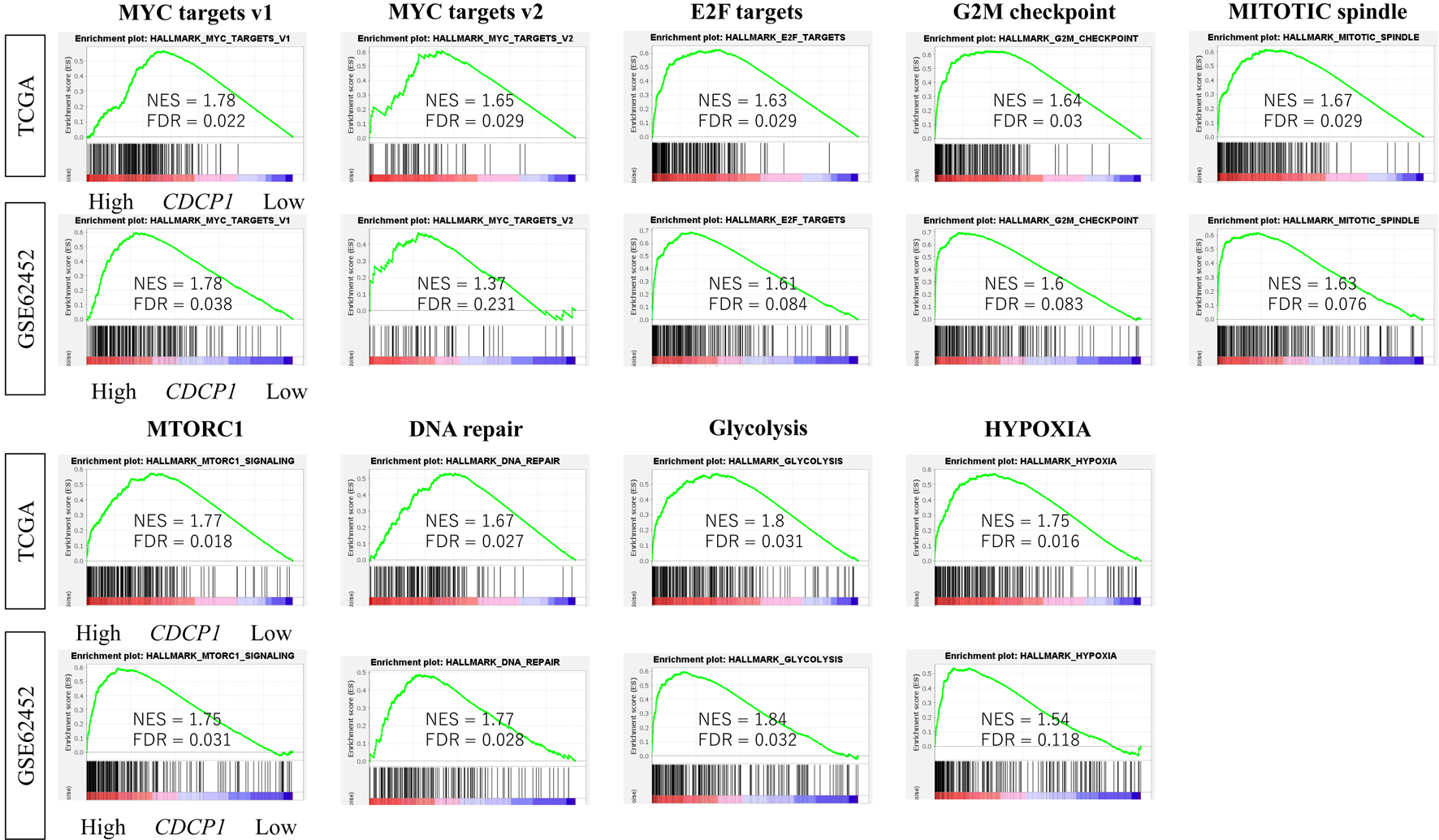
Figure 4. Enrichment of oncogenic signaling pathways in high CDCP1 PDAC. Comparison of Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA) scores for hallmark pathways including MYC targets v1/v2, E2F targets, mitotic spindle, G2M checkpoint, mTORC1, DNA repair, PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling, glycolysis, and hypoxia, between high CDCP1 and low CDCP1 tumors in the TCGA and GSE62452 cohorts.
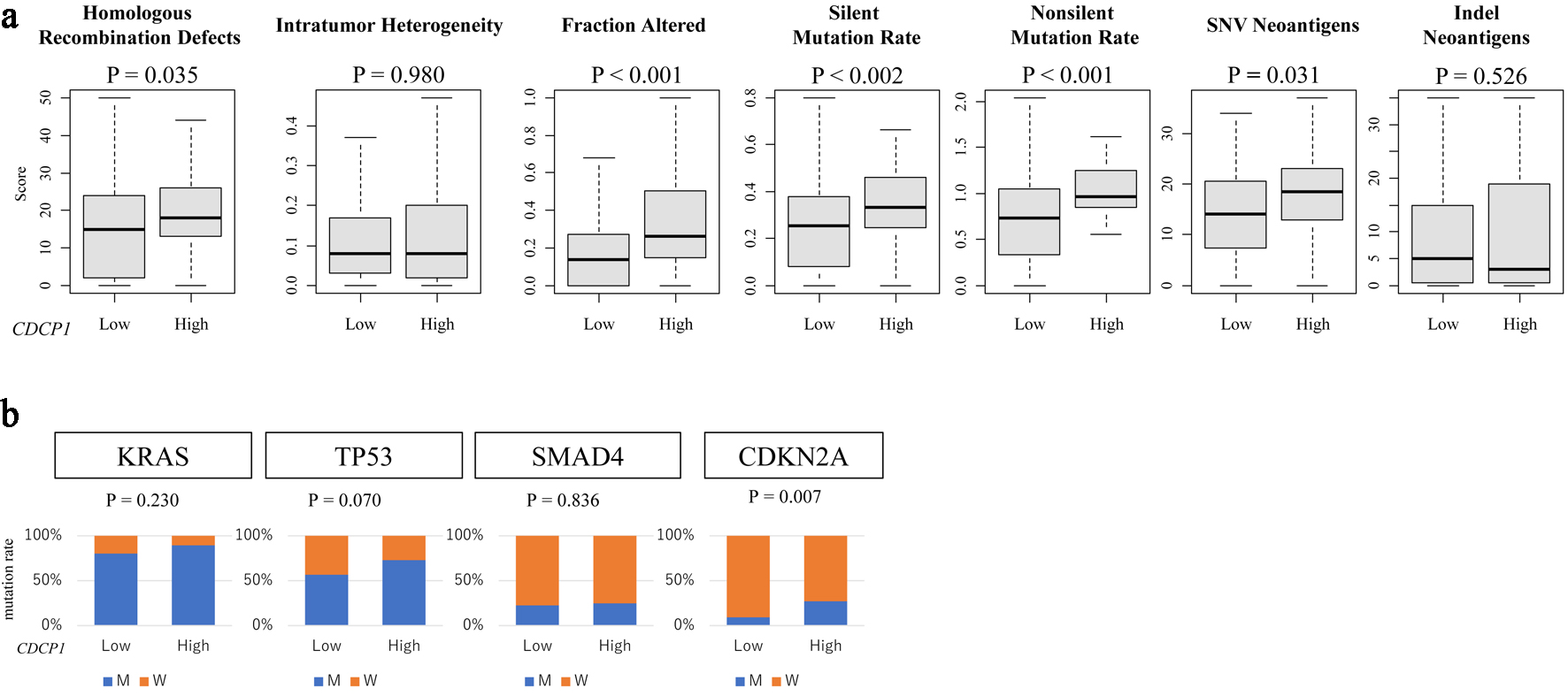
Figure 5. CDCP1 expression is associated with genomic instability and specific gene mutations. (a) Genomic instability metrics including silent and non-silent mutation rates, single nucleotide variant (SNV) and indel neoantigen loads, fraction altered, intratumor heterogeneity, and homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) scores across CDCP1 expression groups. (b) Bar plots of mutation frequency for key PDAC driver genes (KRAS, TP53, SMAD4, and CDKN2A) in high CDCP1 and low CDCP1 tumors in the TCGA cohort.




