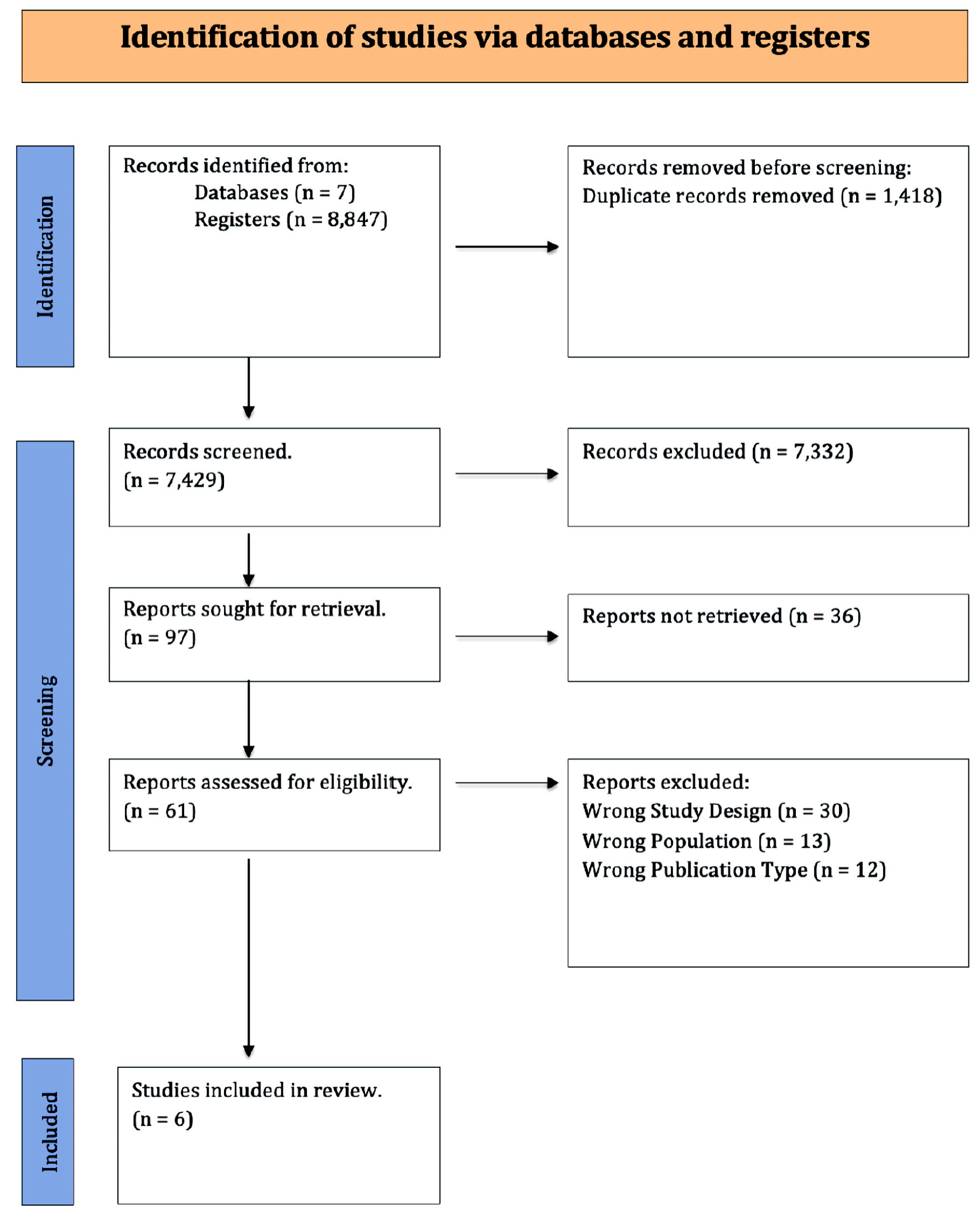
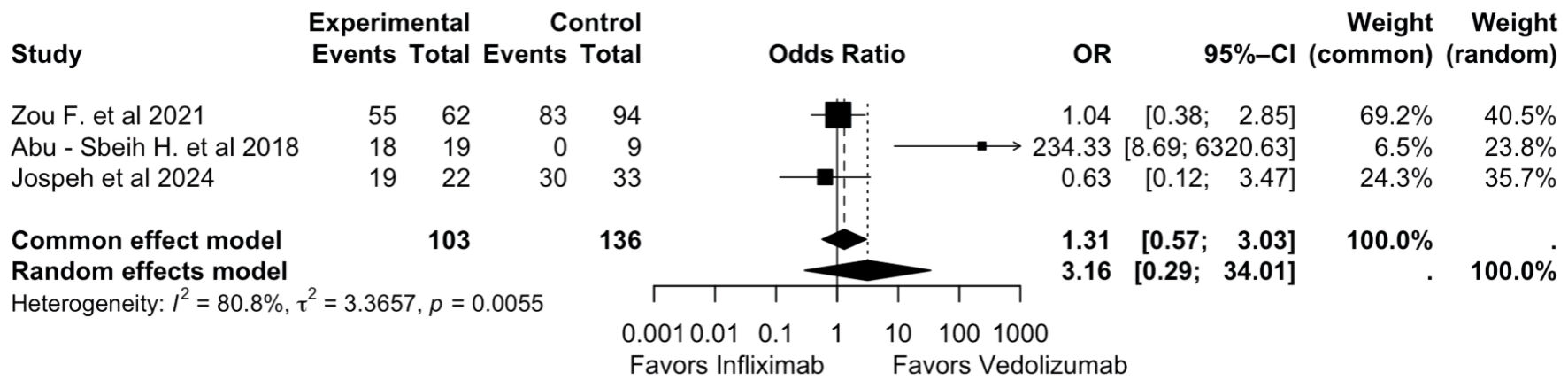
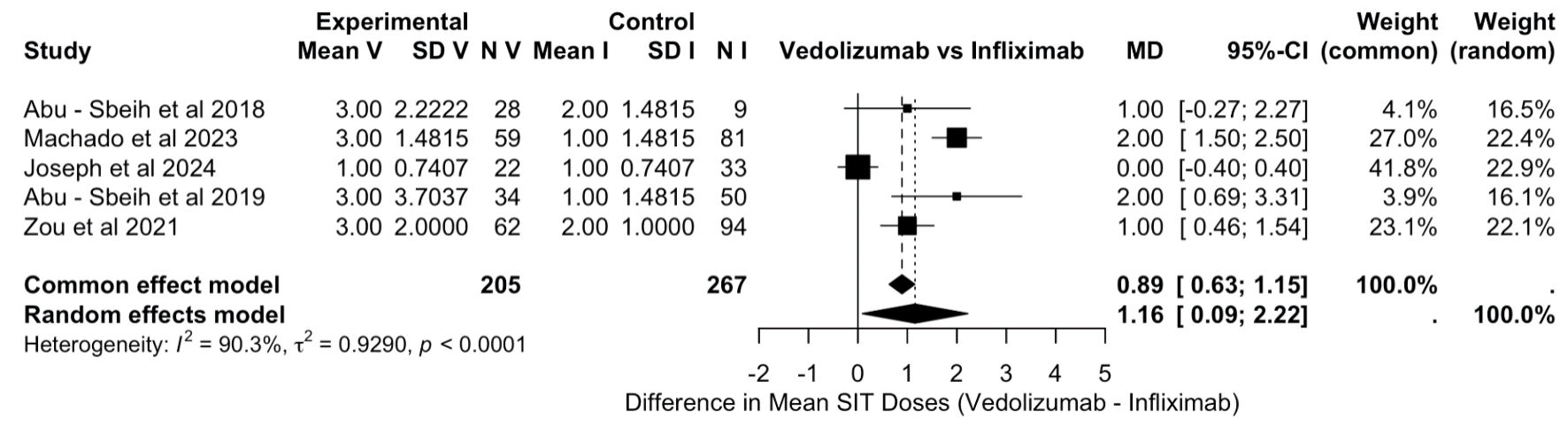
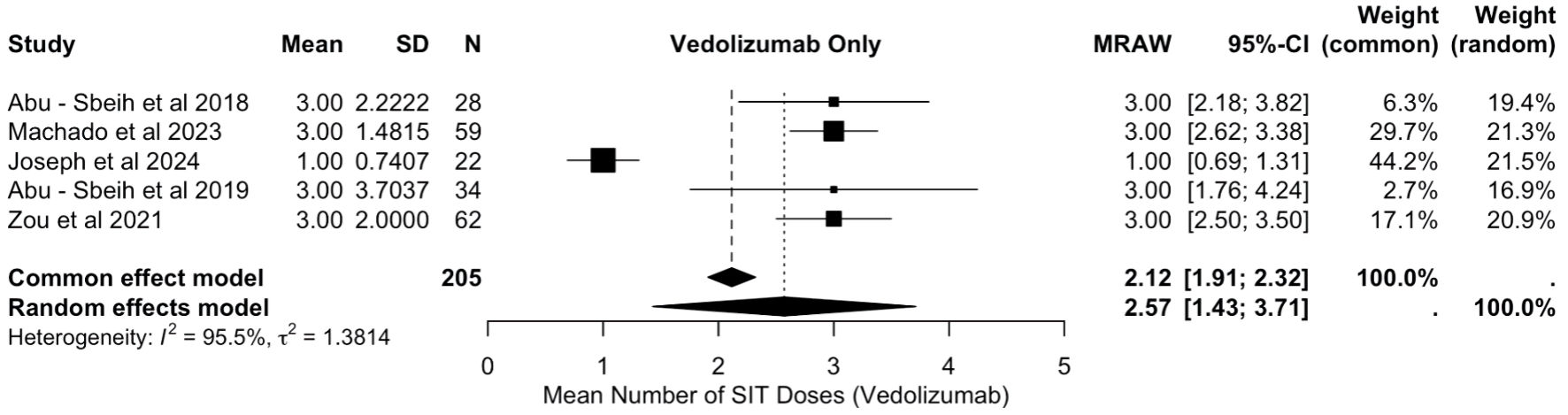
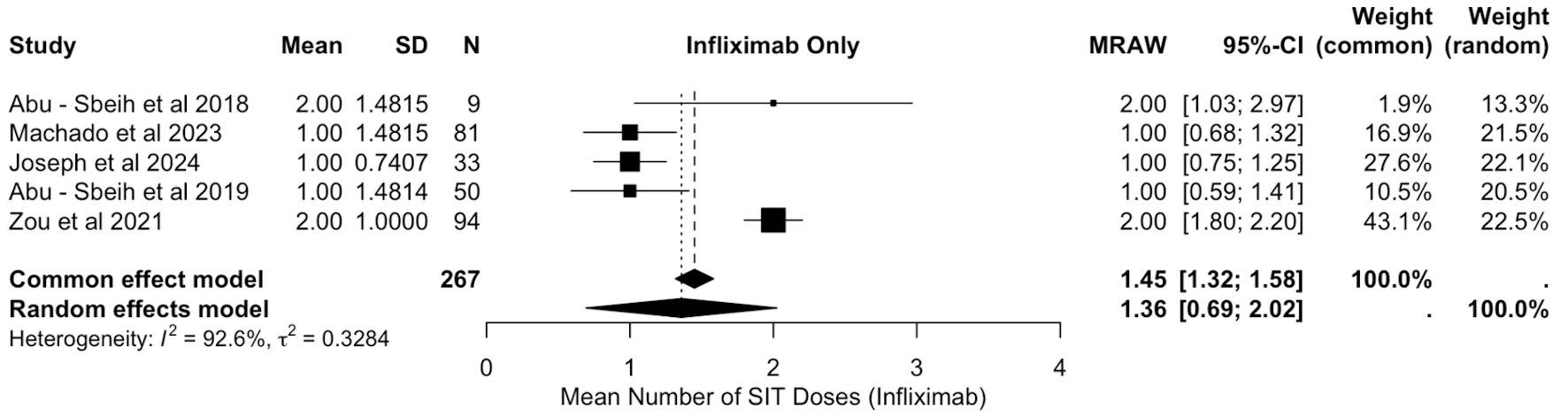
Figure 1. PRISMA flowchart. PRISMA: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.
| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://wjon.elmerpub.com |
Original Article
Volume 16, Number 4, August 2025, pages 331-341
Efficacy of Infliximab Versus Vedolizumab in the Management of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Figures

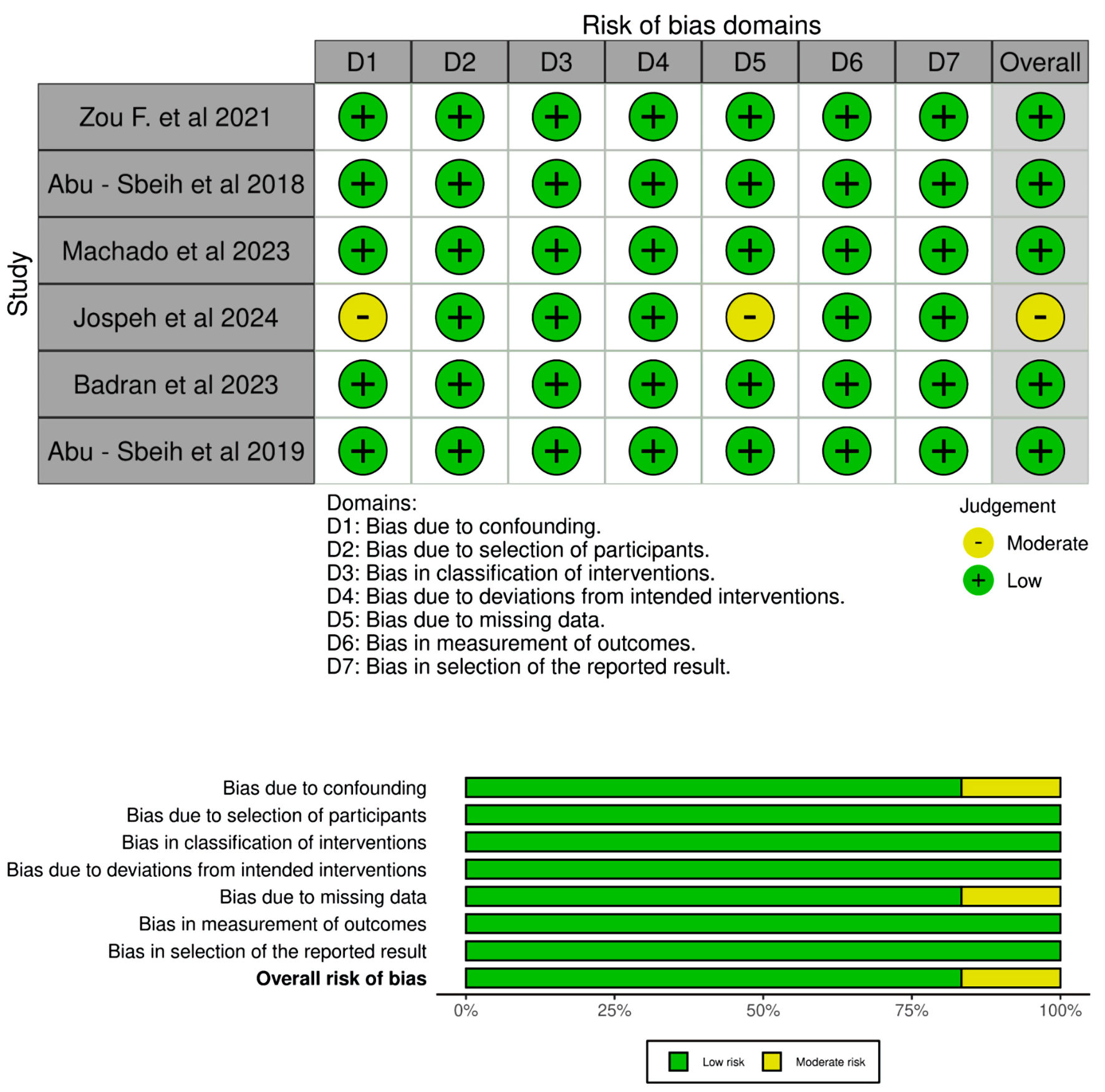
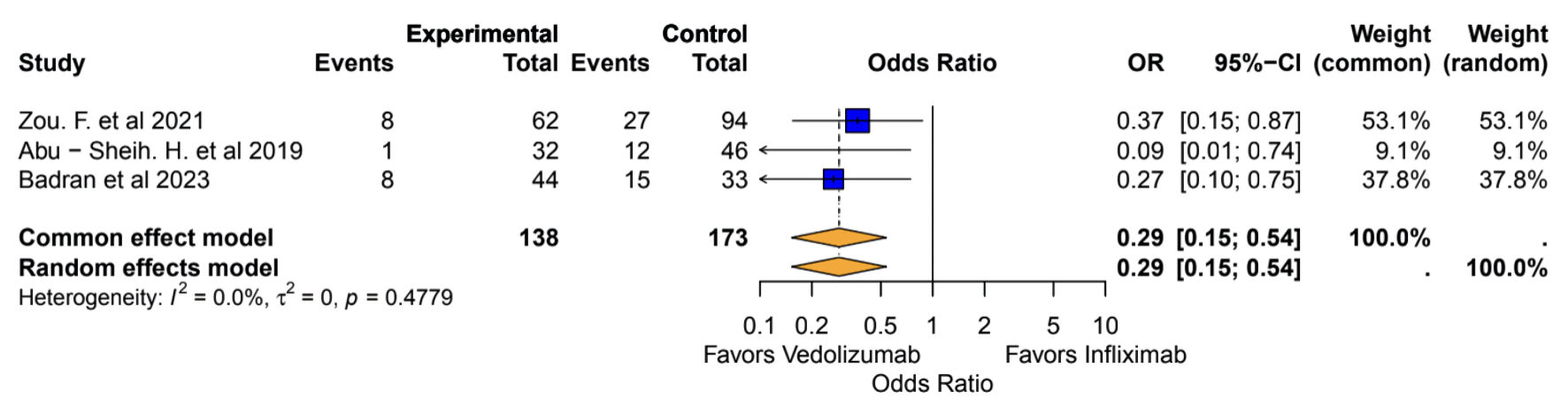
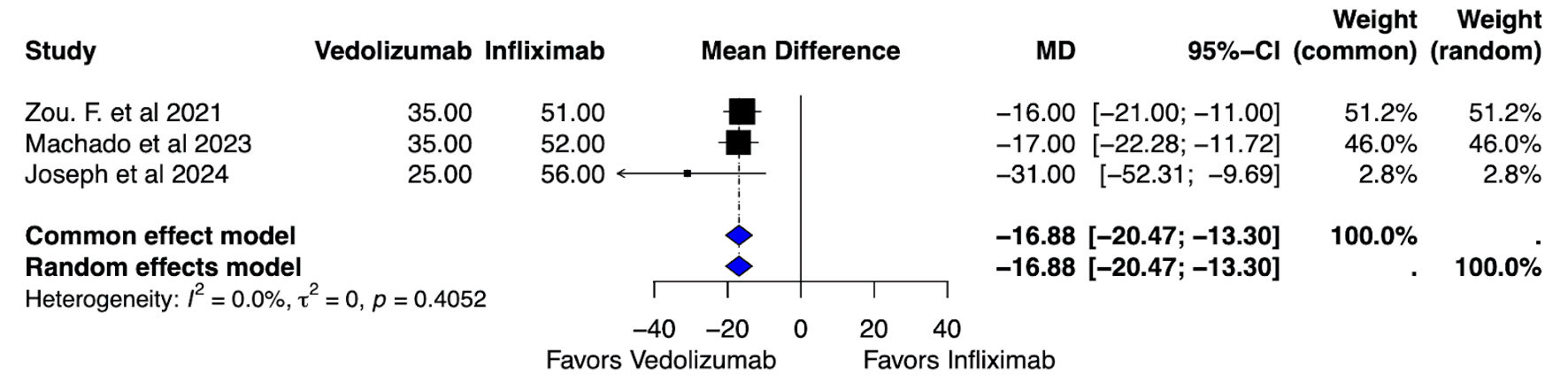
Tables
| Study | Male sex (n) | Median age (years) | White race (n) | Total patients who received SIT (n) | Year | Country | Study design | VDZ only (n) | IFX only (n) | IFX f/b VDZ (n) | VDZ f/b IFX (n) | Types of cancer (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC: retrospective cohort; N/A: not available; VDZ: vedolizumab; IFX: infliximab; f/b: followed by; GU: genitourinary; GI: gastrointestinal; RCC: renal cell carcinoma. | ||||||||||||
| Zou et al, 2021 [18] | 118 | 64 | 169 | 184 | 2021 | USA | RC | 62 | 94 | 28 | 0 | Melanoma: 54 |
| GU cancer: 49 | ||||||||||||
| Lung cancer: 26 | ||||||||||||
| Others: 27 | ||||||||||||
| Stage 3: 26 | ||||||||||||
| Stage 4: 130 | ||||||||||||
| Abu-Sbeih et al, 2019 [19] | 66 | 60 | 76 | 84 | 2019 | USA | RC | 32 | 46 | 4 | 2 | Melanoma: 40 |
| GU cancer: 28 | ||||||||||||
| Thoracic, head and neck cancer: 11 | ||||||||||||
| Stage 4: 72 | ||||||||||||
| Badran et al, 2023 [20] | 42 | 61.3 | N/A | 77 | 2023 | USA | RC | 44 | 33 | 0 | 0 | Melanoma: 35 |
| GU cancer: 14 | ||||||||||||
| Lung/head/neck cancer: 15 | ||||||||||||
| GI cancer: 6 | ||||||||||||
| Endocrine: 1 | ||||||||||||
| Other: 6 | ||||||||||||
| Stage: N/A | ||||||||||||
| Machado et al, 2023 [21] | 105 | 63 | 139 | 156 | 2023 | USA | RC | 59 | 81 | 16 | 0 | Melanoma: 70 |
| GU cancer: 53 | ||||||||||||
| Thoracic/head and neck cancer: 20 | ||||||||||||
| GI cancer: 6 | ||||||||||||
| Hematological: 3 | ||||||||||||
| Other: 5 | ||||||||||||
| Stage 3: 22 | ||||||||||||
| Stage 4: 134 | ||||||||||||
| Joseph et al, 2024 [22] | 29 | 65 | 55 | 55 | 2024 | USA | RC | 22 | 33 | 0 | 0 | Melanoma: 28 |
| Non-melanoma: 27 | ||||||||||||
| Metastatic cancer: 29 | ||||||||||||
| Metastatic: 29 | ||||||||||||
| Abu-Sbeih et al, 2018 [23] | 20 | 63 | N/A | 28 | 2018 | USA | RC | 19 | 9 | 9 | 0 | Melanoma: 7 |
| RCC: 4 | ||||||||||||
| Prostate carcinoma: 4 | ||||||||||||
| Urothelial cancer: 3 | ||||||||||||
| Other solid tumors: 10 | ||||||||||||
| Stage 3: 6 | ||||||||||||
| Stage 4: 22 | ||||||||||||
| Study | Outcomes | ICI type | SIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-CTLA-4 (n) | Combined (n) | Anti PD (L)-1 (n) | VDZ (n) | IFX (n) | ||
| aCTLA-4 alone or in combination. ICI: immune checkpoint inhibitor; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4; VDZ: vedolizumab; IFX: infliximab; SIT: selective immunosuppressive therapy; SD: standard deviation; IQR: interquartile range. | ||||||
| Zou et al, 2021 [18] | Remission, recurrence, median duration of steroid exposure, mean doses of SIT | 23 | 55 | 78 | 3 (SD: 2) | 2 (SD: 1) |
| Abu-Sbeih et al, 2019 [19] | Recurrence, mean doses of SIT | 21 | 30 | 33 | 3 (IQR: 1 - 6) | 1 (IQR: 1 - 3) |
| Badran et al, 2023 [20] | Recurrence | 3 | 42 | 32 | N/A | N/A |
| Machado et al, 2023 [21] | Median duration of steroid exposure, mean doses of SIT | 26 | 62 | 68 | 3 (IQR: 2 - 4) | 1 (IQR: 1 - 2) |
| Joseph et al, 2024 [22] | Recurrence, median duration of steroid exposure, mean doses of SIT | 20a | 35 | 1 (IQR: 1 - 2) | 1 (IQR: 1 - 2) | |
| Abu-Sbeih et al, 2018 [23] | Remission, mean doses of SIT | 8 | 8 | 12 | 3 (IQR: 1 - 4) | 2 (IQR: 1 - 3) |