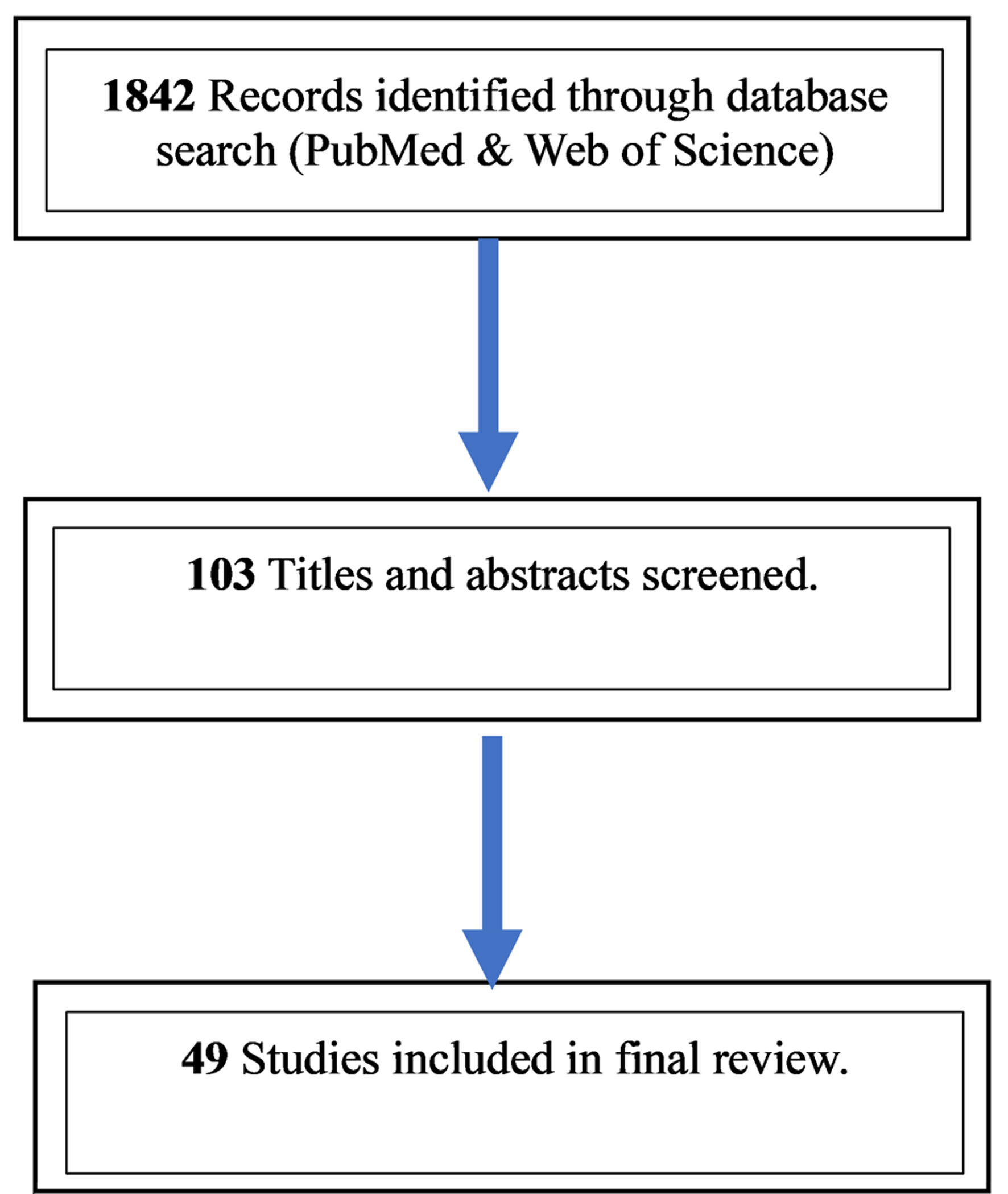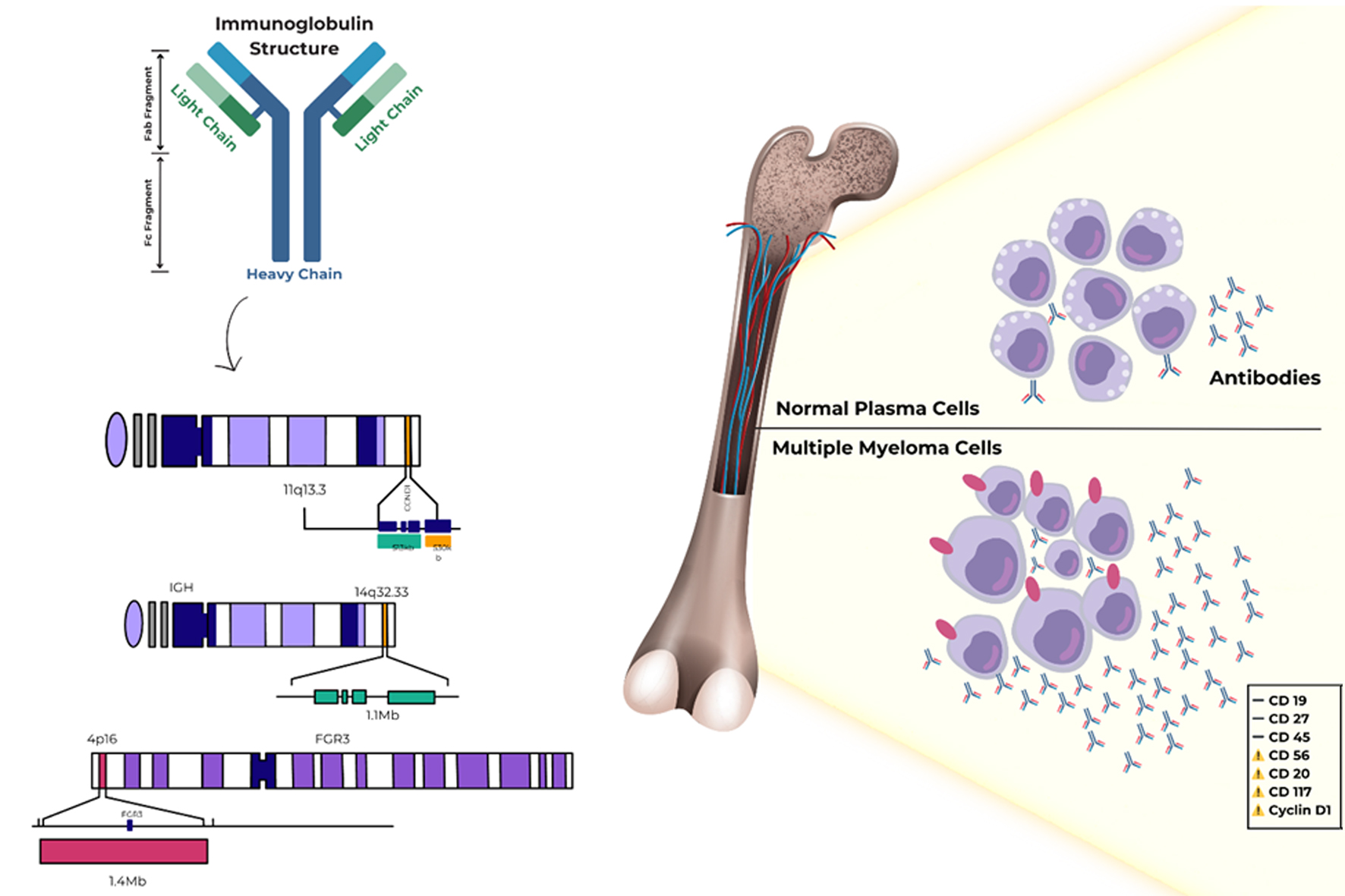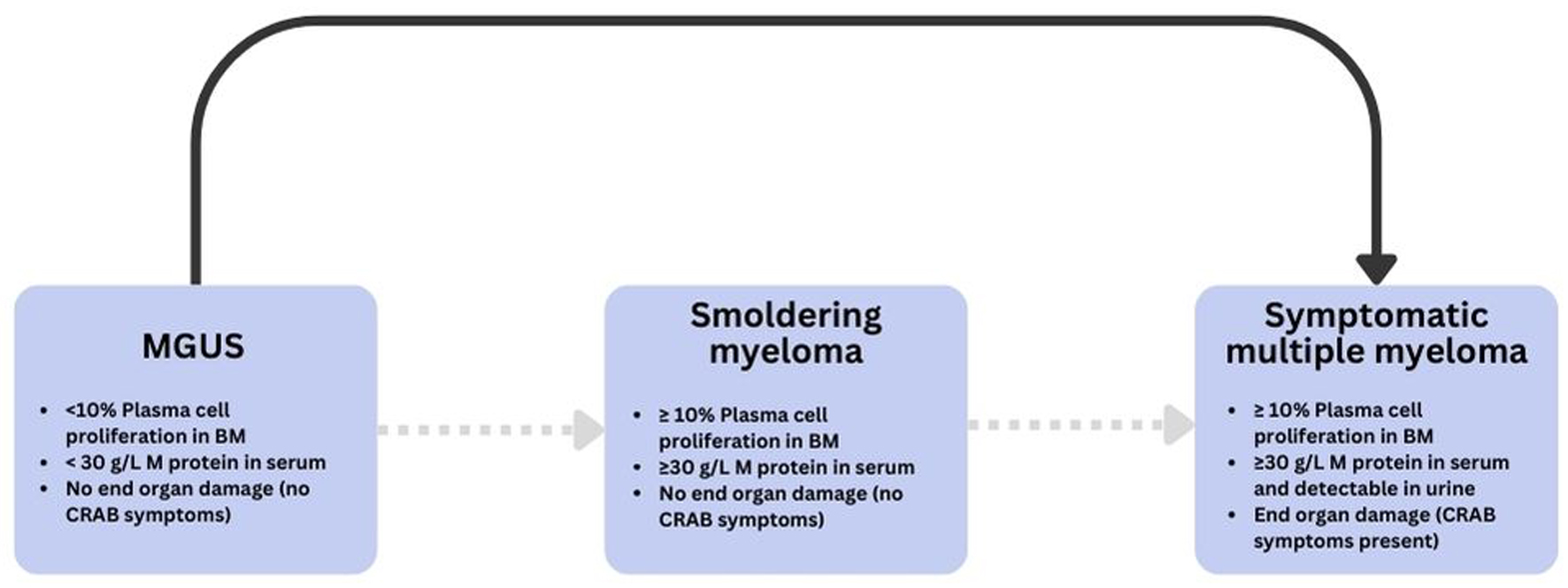
Figure 1. Progression and diagnostic criteria across the monoclonal gammopathy spectrum. Schematic overview of MGUS, smoldering myeloma, and symptomatic multiple myeloma with key thresholds (clonal plasma cells in bone marrow, serum M-protein) and CRAB/end-organ damage criteria [9]. BM: bone marrow; CRAB: hypercalcemia, renal insufficiency, anemia, bone lesions; MGUS: monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance.