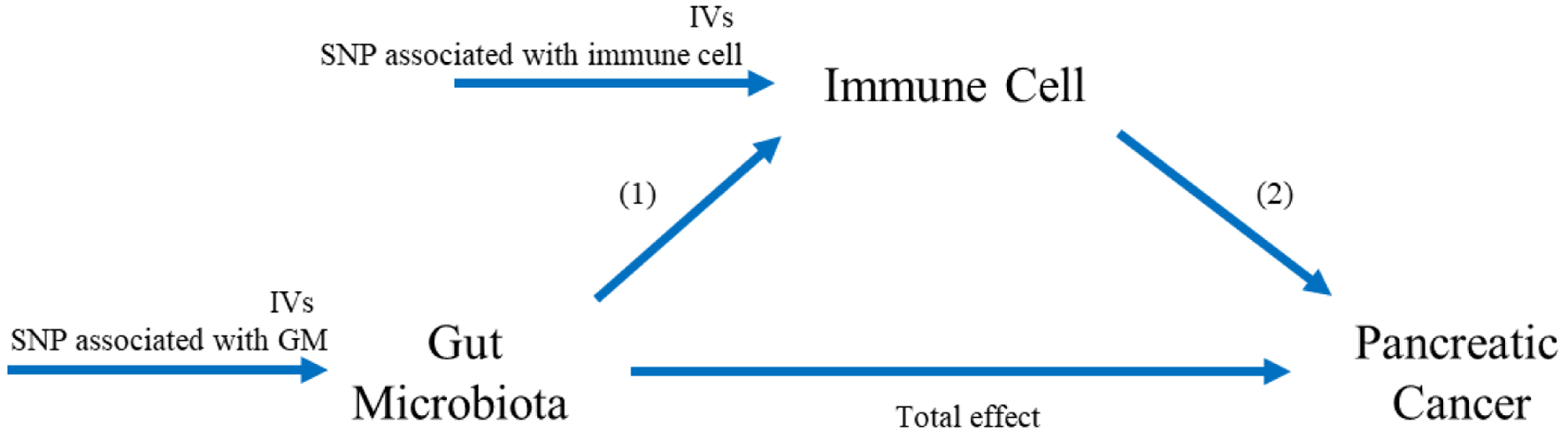
Figure 1. The study design. A two-step Mendelian randomization study of GM on PC mediated by immune cell. IVs: instrumental variables; SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism.
| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.wjon.org |
Original Article
Volume 15, Number 6, December 2024, pages 922-928
Causal Relationships Between Gut Microbiota, Immune Cell and Pancreatic Cancer: A Two-Step, Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
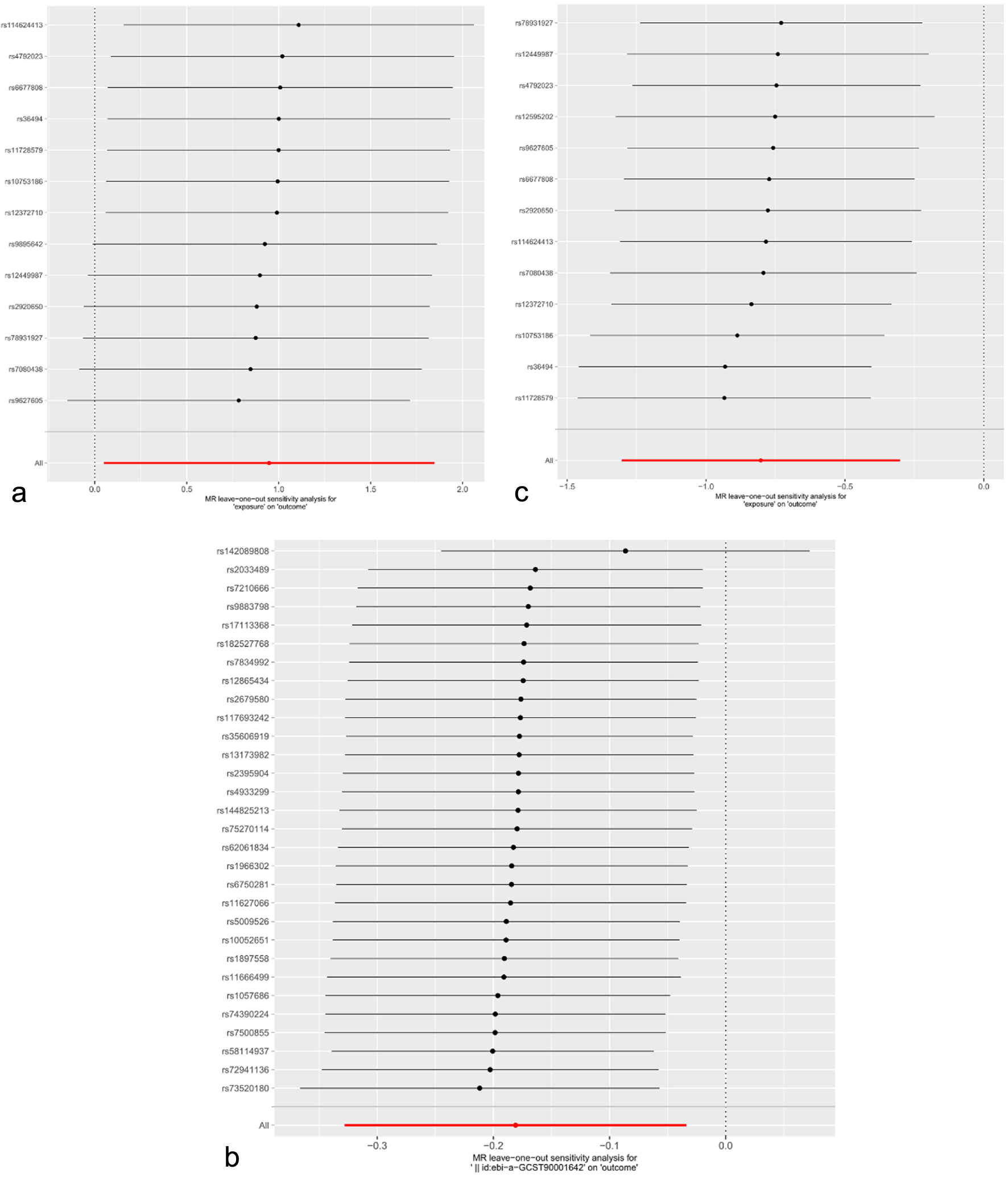
Figures

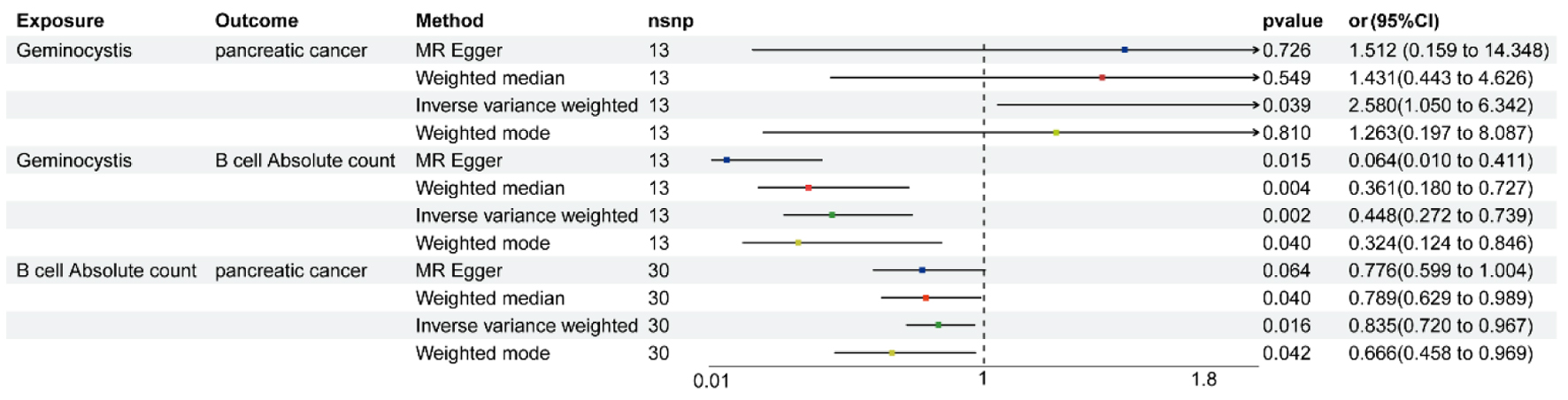
Table
| Total effect β | Direct effect A β | Direct effect B β | Mediation effect β | Mediated proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total effect: The causal role of GM on PC. Direct effect A: The causal role of GM on immune cell traits. Direct effect B: The causal role of immune cell traits on PC. β(Indirect effect) = β(Direct effect A) × β(Direct effect B). The mediated proportion = β(indirect effect)/β(total effect). GM: gut microbiota; PC: pancreatic cancer. | ||||
| 0.948 | -0.803 | -0.181 | 0.145 | 15.321 |